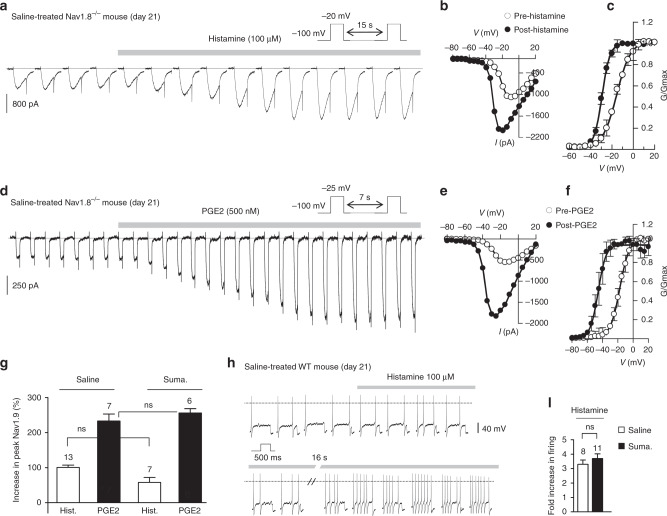
Fig. 7.
Mast cell mediators activate Nav1.9 in dural afferent neurons. a Nav1.9 current challenged with 100 µM histamine in a DiI+ dural afferent neuron from a saline-treated Nav1.8−/− mouse. CsCl-only-based patch pipette solution. b I–V relationships from the cell depicted in a determined before and after histamine exposure. c Averaged activation curve for Nav1.9 determined before and after histamine application in DiI+ neurons (n = 13). Single Boltzmann fits gave V1/2 values of −15 ± 0.3 and −29.3 ± 0.15 mV before and after histamine application, respectively. d Nav1.9 current challenged with 500 nM PGE2 in a DiI+ dural afferent neuron from a saline-treated Nav1.8−/− mouse. CsCl-only-based patch pipette solution. e I–V relationships from the cell depicted in d determined before and after PGE2 exposure. f Averaged activation curve for Nav1.9 determined before and after PGE2 application in DiI+ dural afferent neurons (n = 7). Single Boltzmann fits gave V1/2 values of −17.3 ± 0.6 and −45.6 ± 1.1 mV before and after PGE2 application, respectively. g Increase in Nav1.9 current (at peak I/V as in b and e) induced by histamine in DiI+ neurons from saline-treated or sumatriptan-treated Nav1.8−/− mice. ns not significant, Mann–Whitney test. h Effects of histamine on a DiI+ dural afferent neuron from a WT mouse treated with saline solution. Voltage responses were evoked by depolarizing pulses (+50 pA) applied every 8 s. KCl-based intracellular solution. i Mean increase in firing of dural afferent neurons in response to histamine from WT mice treated with sumatriptan or the saline solution. ns not significant, Mann–Whitney test