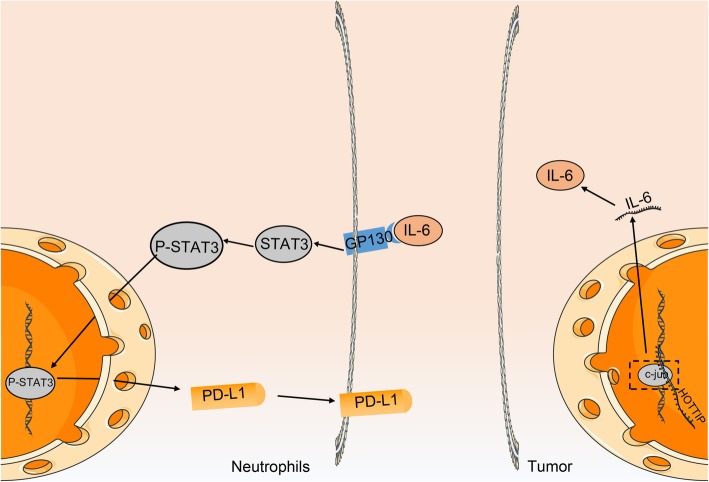
Fig. 7.
The schematic diagram depicts the regulatory mechanism of HOTTIP in the immune escape of OC cells. In OC cells, high expression of HOTTIP can enhance the expression and secretion of IL-6 from OC cells by promoting the transcription of IL-6. The secreted IL-6 stimulates the expression of PD-L1 by binding to the IL-6 receptor on the surface of neutrophils around the cancer cells and then activates the STAT3 pathway, thus increasing the expression of PD-L1 on the surface of neutrophils and inhibiting the activity of T cells, which further promotes apoptosis, thus facilitating the immune escape of OC cells