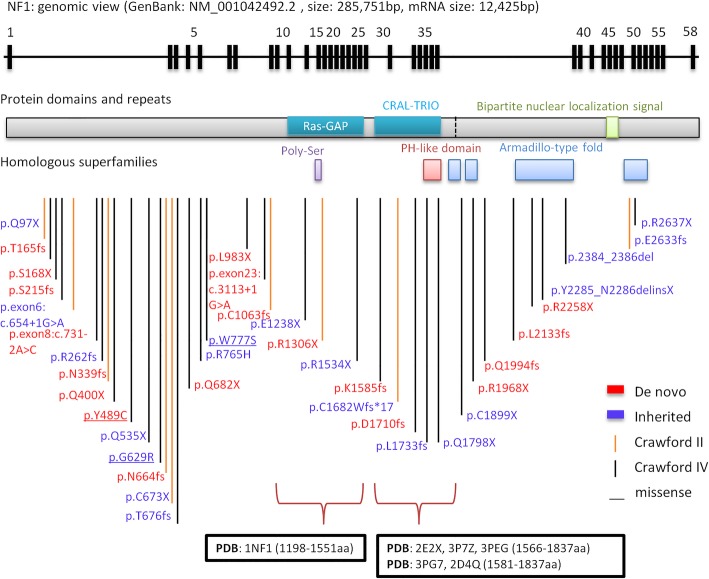
Fig. 2.
NF1 pathogenic variants identified by WES in genomic and protein view. NF1 pathogenic variants view from genome to protein secondary structure and domain. Genomic view: showing in the top with black bars marked as the relative position of exons from NF1 gene transcript variant 1 (GenBank: NM_001042492.2). NF1 pathogenic variants map: NF1 pathogenic variants identified in this study are marked at the bottom according to the relative position of protein amino acids. NF1 de novo variants show the amino acid change label in red color; inherited variants show in purple color. Vertical lines show variant position, and Crawford type IV shows in black color, Crawford type II shows in orange color. Protein domains and repeats, homologous superfamilies (InterPro: P21359): Ras GAP domain (1187-1557aa, glaucous bar), CRAL-TRIO lipid-binding domain (1580-1738aa, glaucous bar), Bipartite nuclear localization signal domain (2555-2571aa, green bar), Ploy-Ser domain (1352-1355aa, purple bar), PH-like domain superfamily (1727-1837aa, red bar), Armadillo-type fold superfamily (1849-1886aa, 1920-1984aa, 2200-2420aa and 2613-2676aa, blue bar). Ras GAP and CRAL-TRIO lipid binding domains with PDB structure are marked at the bottom showing amino acid positions and PDB accessions