Figure 1.
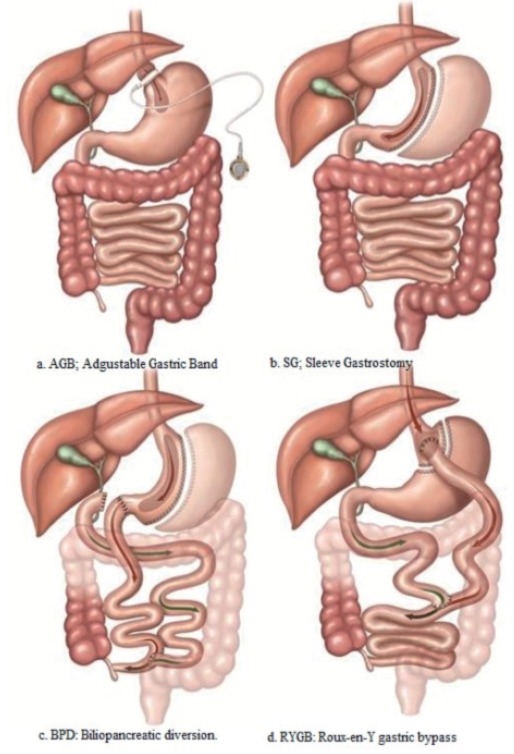
Commonly performed surgical methods for bariatric surgery a) AGB - Adjustable gastric band. A band with an inner inflatable silastic balloon is placed around the proximal stomach just below the gastroesophageal junction. The band is adjusted through a subcutaneous access port by the injection or withdrawal of solution. b) SG - Sleeve gastrectomy. The stomach is transected vertically creating a gastric tube and leaving a pouch of 100 to 200 mL. c) BPD - Biliopancreatic diversion. A 400 mL gastric pouch is formed from the stomach. The small bowel is divided 250 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve and is connected to the gastric pouch to create a Roux-en-Y gastroenterostomy. An anastomosis is performed between the excluded biliopancreatic limb and the alimentary limb 50 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve. d) RYGB - Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. An upper gastric pouch, of 15 to 30 mL in volume, and a lower gastric remnant is formed from the stomach. The jejunum is divided some 30 to 75 cm distal to the ligament of Treitz, and anastomosed to the gastric pouch. The distal jejunum is brought up as a ‘Roux-limb’. The excluded biliary limb, including the gastric remnant, is anastomosed to the bowel some 75 to 150 cm distal to the gastrojejunostomy.78
