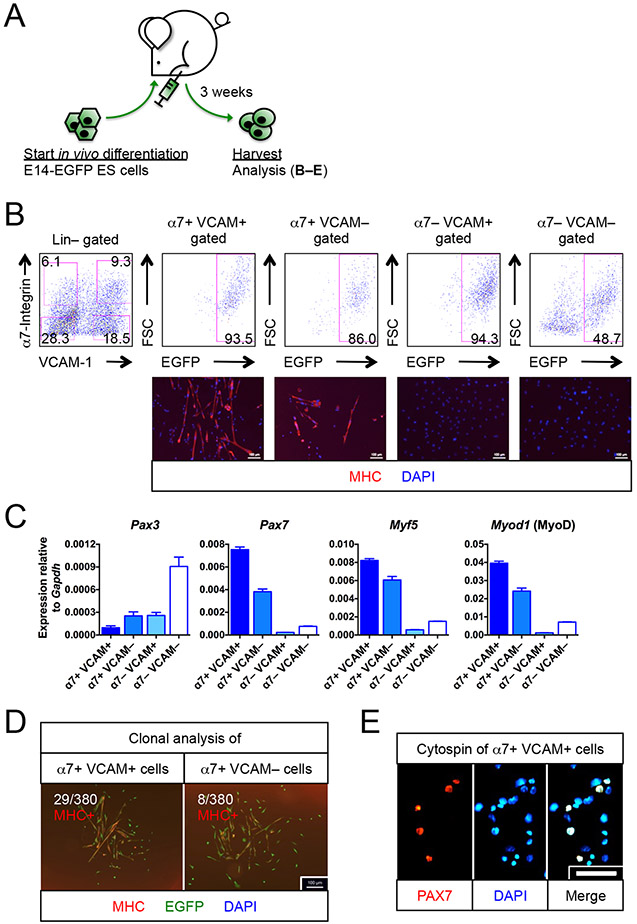
Figure 1. Myogenic progenitors are found in teratomas.
(A)Schematic of generating myogenic progenitors from EGFP-labeled E14 (E14-EGFP) ES cells in vivo.
(B) E14-EGFP ES cell-derived myogenic progenitors. FACS profiling (top row) of 3 week-old teratomas revealed the presence of α7+ VCAM+ and α7+ VCAM− putative myogenic progenitors. Immunostaining (bottom row) confirmed their myogenic identity (MHC+) (n=6 biological replicates). The other 2 fractions, α7− VCAM+ and α7− VCAM−, had minimal myogenic potentials (n=4 biological replicates). Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(C) Quantitative RT-PCR for markers for muscle stem cells (Pax3, Pax7), activated myogenic progenitor cells (Myf5) and myogenic-committed cells (Myod1) (n=6, from 2 biological replicates). Note that Pax3 is also a marker of neuroectoderm derivatives.
(D) Clonal analysis showing that single α7+ VCAM+ or α7+ VCAM− cells were capable of forming MHC+ myogenic colonies with differentiated myoblasts and multi-nuclei myotubes. Ratio indicates number of colonies developed per number of single cells seeded (n=5 biological replicates). Scale bar represents 100 μm.
(E) Cytospins of α7+ VCAM+ cells showing that 30% of which expressed PAX7+, a muscle stem cell transcription factor (n=4 biological replicates). Scale bar represents 100 μm.
α7, α7-integrin. VCAM, VCAM-1. ES cells, embryonic stem cells. Lin, lineage cocktail comprising antibodies against CD45 (hematopoietic) and CD31 (endothelial). MHC, myosin heavy chain. Mean ± SEM is shown in (C). See also Figure S1.