Fig. 2.
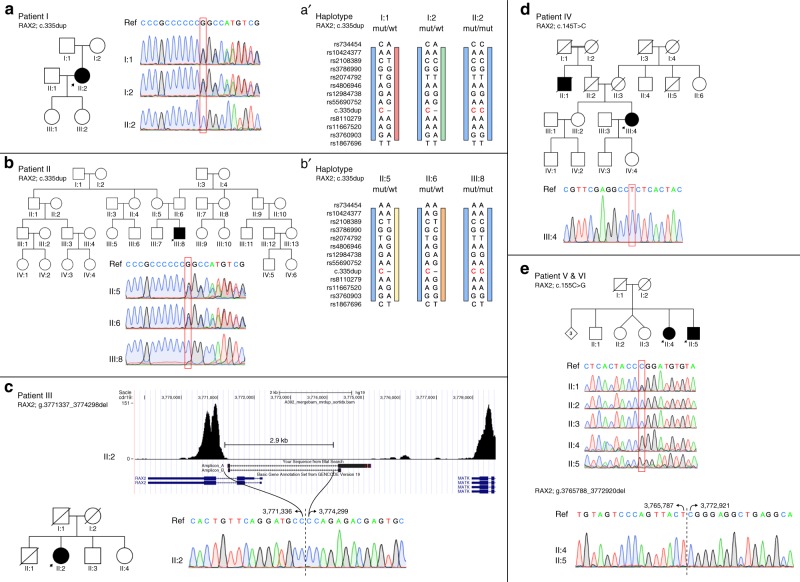
Overview of identified RAX2 variants in five families with ARRP. a Pedigree of patient I, in which RAX2 variant c.335dup p.(Ala113Glyfs*178) was found. Sanger sequencing traces indicate homozygosity in the patient (II:2) and heterozygosity in the unaffected parents (I:1, I:2). b Pedigree of patient II, in which RAX2 variant c.335dup p.(Ala113Glyfs*178) was found. Sanger sequencing traces indicate homozygosity in the patient (III:8) and heterozygosity in the unaffected parents (II:5, II:6). c Pedigree of patient III, in which homozygous RAX2 deletion g.3771337_3774298del was found. The absence of reads mapped to the first two exons of RAX2 is visible on the exome sequencing coverage plot. The sequence of the junction polymerase chain reaction (PCR) product spanning the 2.9 kb deletion is depicted below. d Pedigree of patient IV, in which RAX2 variant c.145T>C, p.(Ser49Pro) was found. Sanger sequencing traces indicate homozygosity in the patient (III:4). e Pedigree of patient V and VI, in which RAX2 variants c.155C>G p.(Pro52Arg) and g.3765788_3772920del were found. Sanger sequencing traces indicate hemizygosity in the patients (II:4, II:5). One of the three analyzed healthy siblings is heterozygous for the missense variant (II:1), while the other two did not carry this variant (II:2, II:3). The sequence of the junction PCR product spanning the 7.1 kb deletion is depicted below. RAX2 variant nomenclature uses numbering with the A of the initiation codon ATG as +1 based on transcript NM_032753. (a’, b’) Haplotype analysis of the c.335dup RAX2 variant. Genotyping of patients I, II, and both of their unaffected parents, using 24 intragenic single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 3 microsatellites located in a region of 1.4 Mb around the variant. The c.335dup RAX2 variant is indicated in red. The blue bar represents the common disease haplotype, from SNP rs10424377 to SNP rs3760903. The maximal common region in the two families spans 447.3 kb. mut mutant, wt wild type.