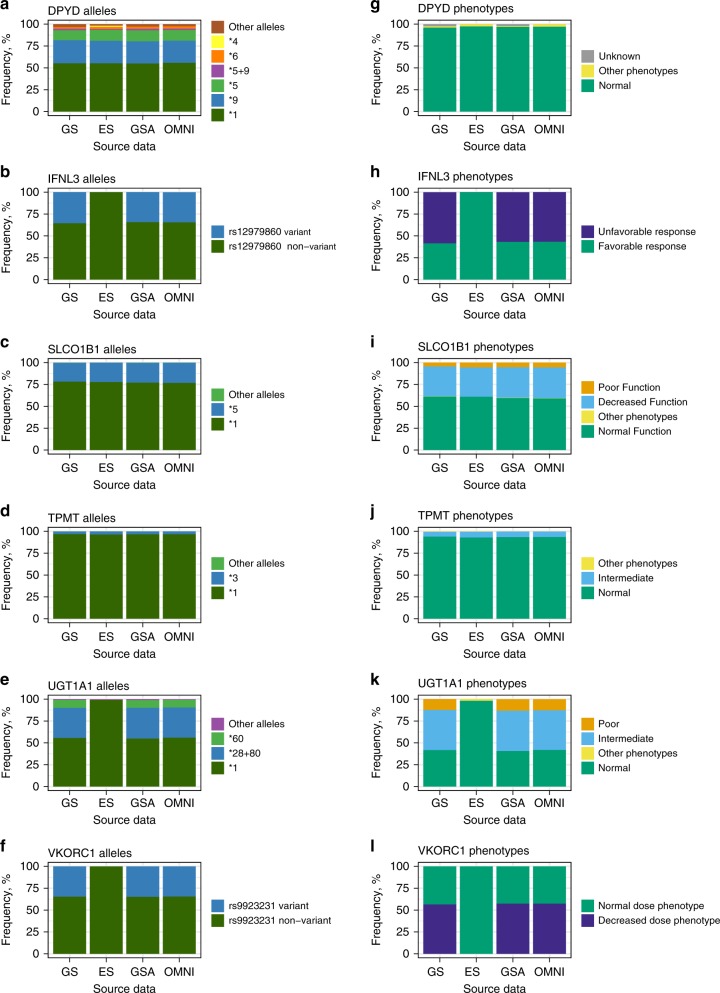
Fig. 3.
Frequencies of predicted alleles and phenotypes by gene and method for non-CYP genes. The results for OMNI and GSA are based on imputed microarray genotype data. The decision to assign an allele a wild-type status (*1) is based upon a genotyping test that interrogates only the most common and already-proven sites of functional variation. In human DNA, it is always possible that a new, previously undiscovered (and therefore uninterrogated) site of variation may confer loss of function in an individual, and thus lead to the rare possibility of a nonfunctional allele being erroneously called as wild type. Alleles and phenotypes with frequencies below 2% are marked as “Other” for better visualization. ES exome sequencing, GS genome sequencing, GSA Global Screening Array, OMNI HumanOmniExpress.