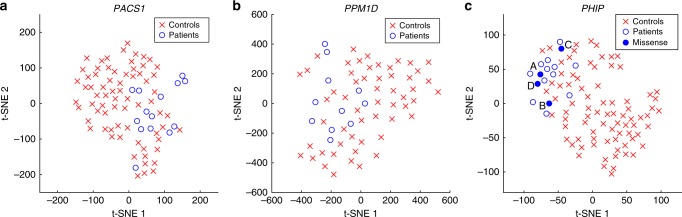
Fig. 1.
Distribution of the hybrid facial features in the PACS1, PPM1D, and PHIP data sets. The t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE) plots of the (a) PACS1, (b) PPM1D, and (c) PHIP data set analyzed using our novel hybrid model show that faces of patients with the same novel intellectual disability (ID) syndrome are located close together within a group of age-, gender-, and ethnicity-matched controls. Four individuals with a missense variant of uncertain significance in the PHIP gene are compared with 12 individuals with a presumed loss-of-function variant in PHIP, showing significant similarity to the PHIP facial phenotype for individuals A and D.