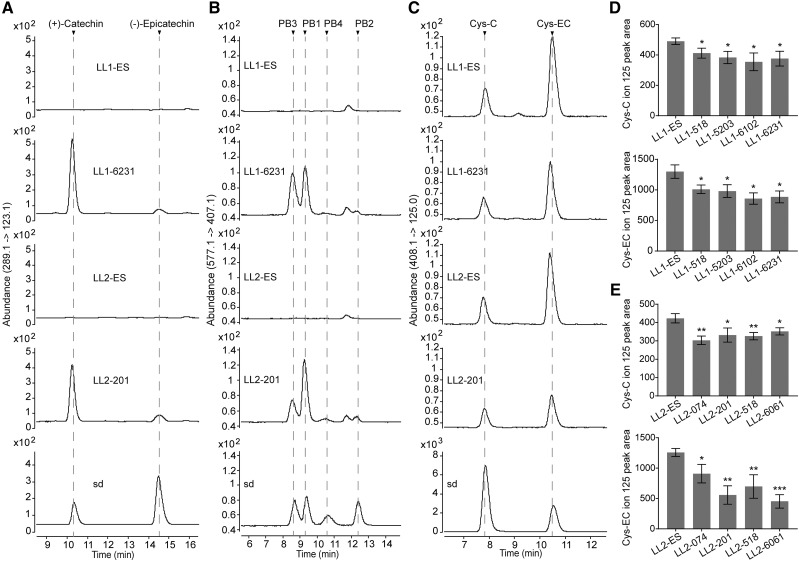
Figure 10.
HPLC-QqQ characterization of the soluble PA fraction in 4 DAP pods of the M. truncatula lar:ldox mutant expressing VvLAR1 (LL1) or VvLAR2 (LL2). Chromatograms for lar:ldox 35S:VvLAR1 line LL1-6231 and 35S:VvLAR2 line LL2-201 are presented here, and their corresponding control (escape) lines are denoted as LL1-ES and LL2-ES, respectively. Chromatograms for the other transgenic lines are presented in Supplemental Figures S4 and S5. A, MRM transition of m/z (289.1 → 123.1) showing that (+)-catechin and (−)-epicatechin accumulate in the young pods of 35S:VvLAR lines but are undetectable in controls. B, MRM transition of m/z (577.1 → 407.1) showing that procyanidin B1, B2, B3, and B4 (PB1 to PB4) accumulate in the young pods of 35S:VvLAR lines but are undetectable in controls. C, MRM transition of m/z (408.1 → 125.0) showing that Cys-C and Cys-EC in the young pods of 35S:VvLAR lines are less abundant than in their corresponding control plants. Cys-C and Cys-EC contents for young pods from each line were measured using the ion peak area at m/z 125.0. D, Cys-C and Cys-EC content in the young pods from control and 35S:VvLAR1 lines. E, Cys-C and Cys-EC content in the young pods from control and 35S:VvLAR2 lines. Data are shown as the mean ± sd (for n = 3 biologically independent samples); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus LL1-ES or LL2-ES, two-tailed Student’s t test.