Figure 1.
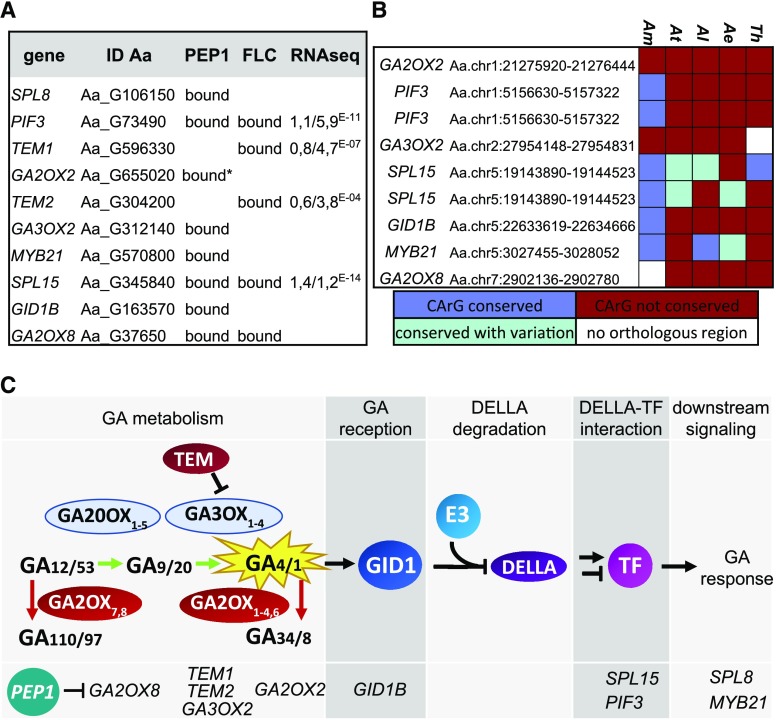
PEP1 binds and regulates genes involved in GA metabolism and signaling. A, List of GA-related genes that were bound or regulated by PEP1. This list includes all genes that were targeted by PEP1 (directly or indirectly as detected by Mateos et al. [2017]) and involved in GA metabolism or direct targets that are part of the Gene Ontology category GO:0009739: response to GA stimulus and have a confirmed function in GA signaling or have a published role in the response to GA. Binding information of FLC was gained in three previous studies (Deng et al., 2011; Mateos et al., 2015, 2017). For genes that were differentially regulated in apices of the pep1 mutant, the log2 (fold change) and P values are given. *, The chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-seq study detected weak binding of PEP1 to GA2OX2 but read enrichment was below the significance threshold. ChIP-qPCR results shown in Supplemental Figure S1, however, suggest that GA2OX2 is a significant target of PEP1. B, Heat map showing the conservation of CArG-boxes in different species. The heat map includes orthologous regions for A. alpina PEP1 BSs associated with GA-related genes in other species. The color code is as follows: dark blue, CArG-box is conserved; light blue, CArG-box is present but sequence varies from A. alpina; dark red, CArG-box is not conserved; and white, no orthologous region was identified. Species are as follows: Arabis montbretiana (Am), Arabidopsis (At), Arabidopsis lyrata (Al), Aethionema arabicum (Ae), and Tarenaya hassleriana (Th). C, Schematic overview of the different steps of the GA pathway. The middle row shows key enzymes involved in each step, and the bottom row lists genes that are targeted by PEP1 in each step.