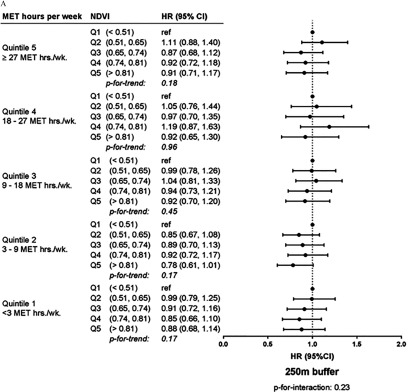
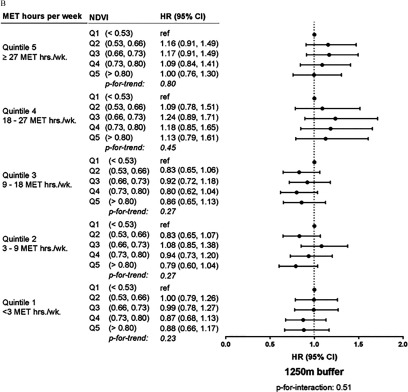
Figure 2.
Stratum-specific hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the effect of residential contemporaneous summer greenness on incident depression within leisure time physical activity levels in the Nurses’ Health Study ( with 3,612 cases over 315,548 person-years of follow-up, 2000–2010). HRs are from stratified models adjusted for age, race, body mass index, smoking status and pack-years of smoking, alcohol consumption, physical function, bodily pain (baseline), marital status, social network strength, care to ill family members (baseline), difficulty sleeping (baseline), baseline mental health, educational attainment, husband’s educational attainment, Census tract population density, Census tract median income, Census tract median home value, and level (USCB 2000). MET, metabolic equivalent of task; NDVI, Normalized Difference Vegetation Index; , particulate matter less than in aerodynamic diameter; Q1, least green quintile. p for interaction from single model with interaction term.