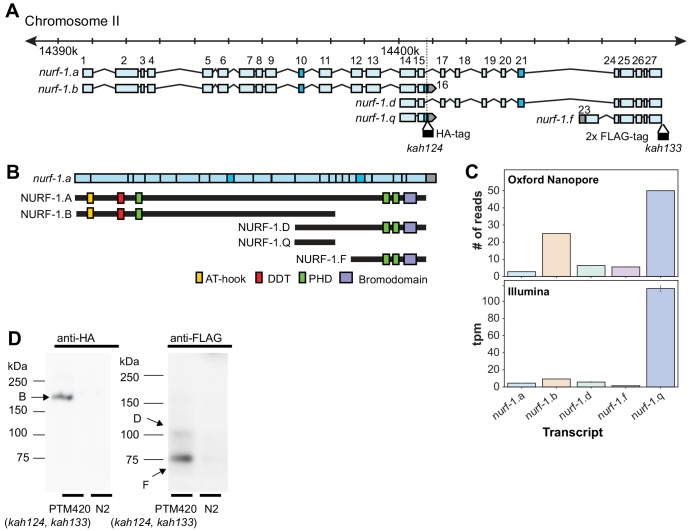
Figure 2. nurf-1 encodes five major transcripts.
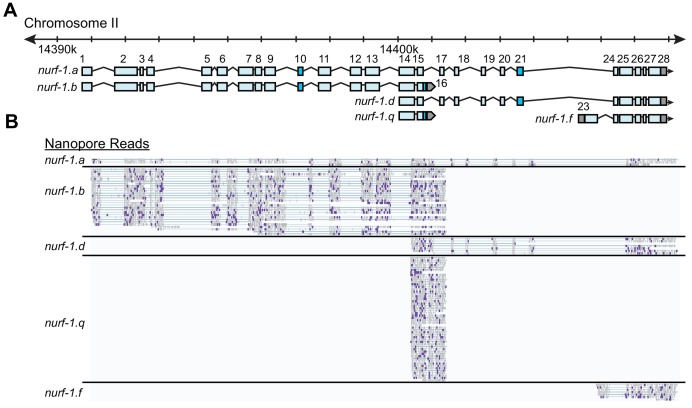
(A) Genomic position of the five nurf-1 transcripts supported by Illumina short read and Oxford Nanopore long reads. Each blue box is an exon. Exon number is indicated on the figure. Dark blue exons (10, 16, and 21) are alternatively spliced, resulting in a 6–9 bp difference in length (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1 for details). Genomic location of the HA and FLAG epitope tag insertion site are shown in black along with their associated allele names. (B) The predicted protein isoforms produced by each of the five major transcripts and along with the domains each isoform contains. Immunoblots only supported translation of the B, D, and F isoforms (see panel D for details). For reference, the spliced nurf-1.a transcript is also shown. (C) Relative expression levels of each transcript, determined by number of Oxford Nanopore reads from a mixed population (top panel) or analysis of Illumina short reads from L2 staged animals using kallisto (bottom reads). tpm = transcripts per million. (D) Western blots of N2 and PTM420 strains. PTM420 contains the HA and FLAG epitope tags shown in panel A. Anti-HA antibody detected a band matching the expected size of the NURF-1.B isoform (arrow). Anti-FLAG antibody detected bands matching the expected size of the NURF-1.D and NURF-1.F isoforms (arrows).
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. RNA-seq analysis of nurf-1.
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. nurf-1 encodes multiple transcripts.
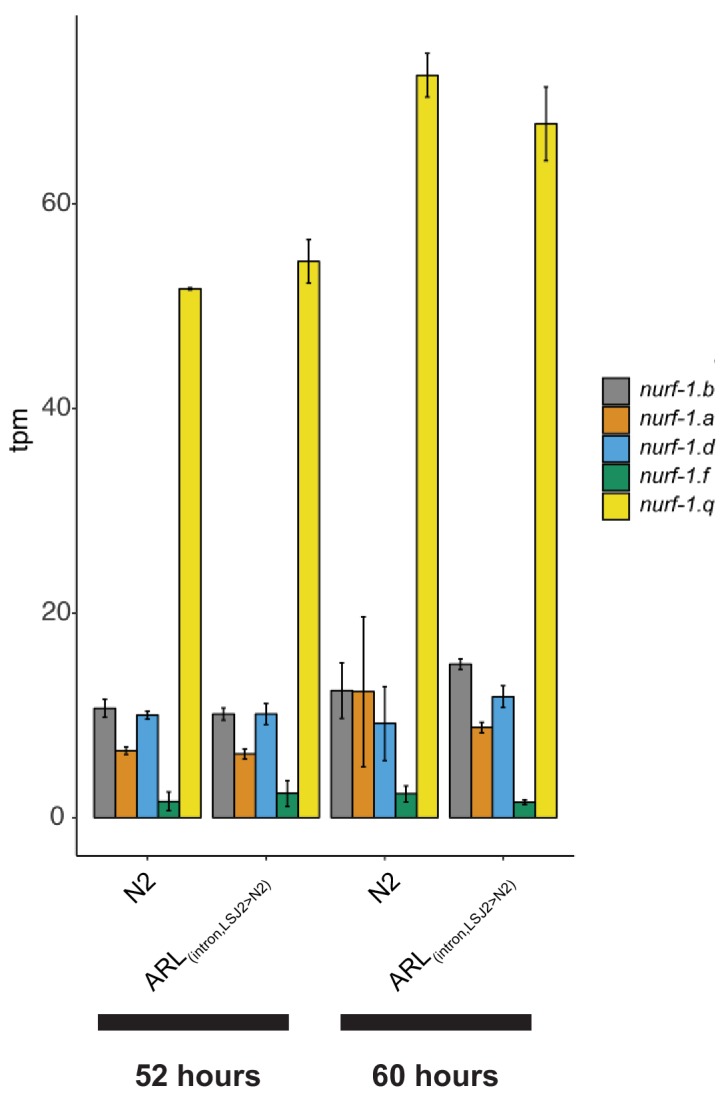
Figure 2—figure supplement 3. Relative expression levels of each nurf-1 transcript, determined by analysis of Illumina short reads using kallisto (bottom reads).