Table 2.
Comparing the characteristics of four soft nanoparticles: nanoliposomes, dendrimers, polymeric micelles, and nanogels. Images reproduced with permission.[126,127]
| Type | Nanoliposomes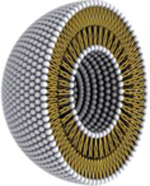
|
Dendrimers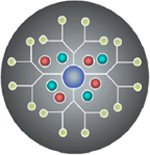
|
Polymeric Micelles
|
Nanogels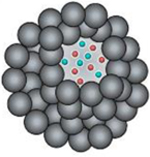
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature | • Natural | • Synthetic | • Synthetic | • Natural • Synthetic |
| Size | • ~50 nm | • 2–15 nm | • 10–100 nm | • <100 nm |
| Preparation methods | • Microfluidization • Extrusion • Sonication |
• Convergent • Divergent |
• Direct dissolution • Film casting • Dialysis • Oil in water emulsion |
• Physical self-assembly of interactive polymers • Chemical synthesis in colloidal environments • Chemical crosslinking of preformed polymers • Template-assisted nanofabrication |
| Adv. | • Biocompatible • Biodegradable • Non-toxic • Non-immunogenic • Controlled and targeted drug delivery • Sustained release • Increase drug efficacy and stability • Many administration routes |
• Biodegradable • Very small size • Well-defined and flexible structure • Precise controllability • High deformability • Stimuli-responsiveness • Surface functionality |
• Small size • Narrow distribution • Easy sterilization • High structural stability • Low toxicity • Excellent blood stability • High water solubility • Controlled release functions |
• Biocompatible • Large surface area • Stimuli sensitivity • High water content/swellability and hydrophilicity • Tunable nanoparticle size • Site targeting • Controllable release • Increased drug stability |
| Disadv. | • Low solubility • Short half-life • High production cost • Difficult sterilization • Lysosomal degradation • Low efficacy active targeting |
• Low biocompatibility • Significant liver accumulation • Material’s homogeneity deterioration • Great batch-to-batch variability |
• Low biocompatibility • Difficult synthesis • Difficult to scale-up • Limited choice of monomers • Concerns over nanotoxicity and storage stability |
• Challenging optimization of degradation mechanism, biodistribution, and component toxicity • Drug instability and rapid degradation in the bloodstream |
| REF. | [92,96,128] | [101,129] | [128,130–132] | [114,127,133] |
