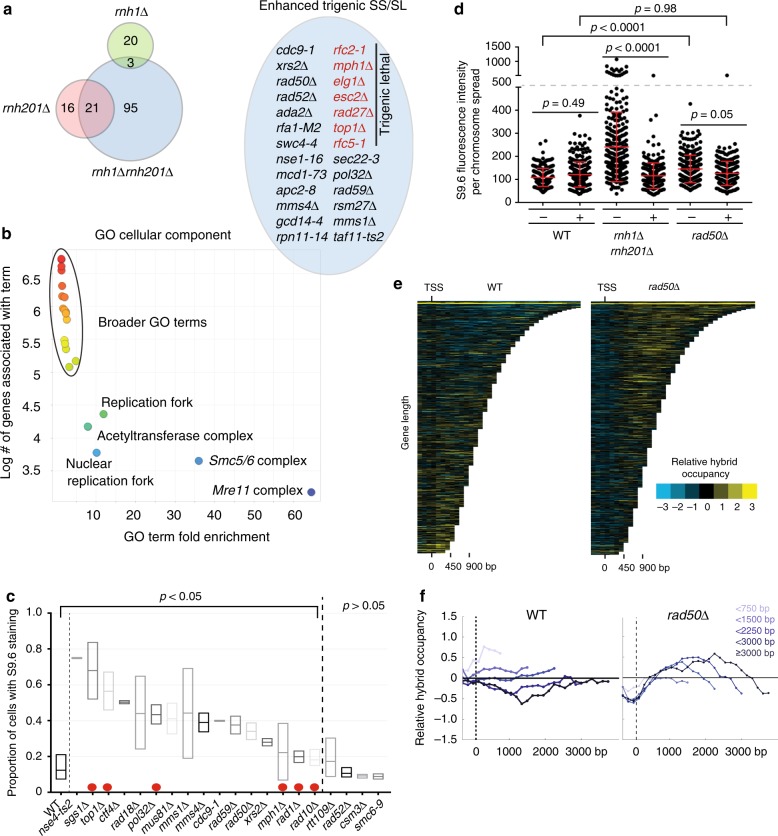
Fig. 1.
RNaseH-deficient yeast depend on replisome function and fork protection for fitness. a Negative genetic interaction results of double and triple mutant SGA screens with the indicated query genotype. A Venn diagram of candidate negative genetic interactions is shown (left) and validated hits that are sicker as triple mutants are in the blue circle. b Gene Ontology analysis of negative rnhΔΔ-interacting partners. Plots show the output of ReviGO, which effectively trims redundant GO terms. c S9.6 staining of chromosome spreads in the indicated strains. Strains between the dotted lines had a significantly higher proportion of stained nuclei than WT (Fisher exact test. p < 0.05, Holm–Bonferroni corrected). Red dots indicate predicted positive controls (see main text). Box plots show the minimum and maximum values with the line at the mean value. d Validation of DNA:RNA hybrid increases in rad50Δ cells. The minus and plus signs indicate that cells were grown without or with an RNH1 overexpression plasmid. e and f Mean genome-wide relative DNA:RNA hybrid occupancy in WT, and rad50Δ as a function of gene length. Profiles were generated in duplicate. Quantile normalized and mean data are shown here. e Chromatra plots showing a heat map of DNA:RNA hybrid levels in WT, and rad50Δ. f A total of 4868 genes were split into the indicated gene length categories (538 genes < 750 bp, 1861 genes < 1500 bp, 1263 genes < 2250 bp, 636 genes < 3000 bp, and 570 genes ≤ 3000 bp) with mean enrichment scores calculated and plotted for each category