Figure 7.
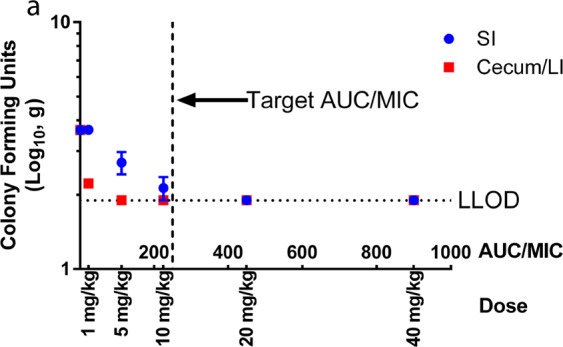
Ciprofloxacin dose response in the mouse model of Shigella infection. Previous studies have established a target ciprofloxacin AUC/MIC ratio of 250 for the treatment of Gram-negative bacterial infections in humans. The efficacy of ciprofloxacin oral doses predicted to generate AUC/MIC values ranging from 22–900 were evaluated in the mouse model of Shigella infection. In agreement with the target AUC/MIC ratio of 250, infected mice with predicted ciprofloxacin AUC/MIC values of ≤225 had detectable S. flexneri infection in the large intestine and/or small intestine. In contrast, mice receiving ciprofloxacin doses of 20 and 40 mg/kg BID (AUC/MIC ratios of 450 and 900, respectively) had no detectable S. flexneri in their gastrointestinal tissue. Values are reported as mean ± SD (n = 3 mice/group).
