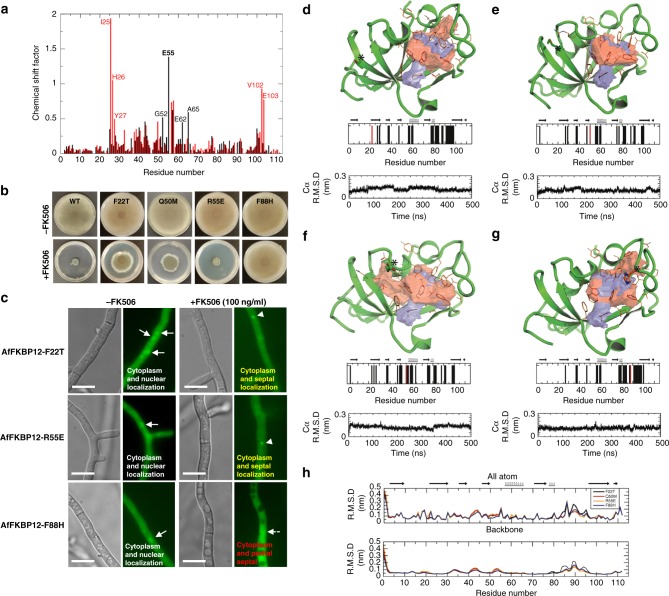
Fig. 2.
Structural implication of AfFKBP12 mutations. a NMR analysis showing chemical shifts induced by FK506 binding to A. fumigatus (red) and human (black) FKBP12. b Growth of the Affkbp12 mutants in the absence and presence of FK506 for 5 days at 37 °C. c Microscopic localization AfFKBP12 mutated proteins in vivo in the absence or presence of FK506. Arrows show nuclear localization of AfFKBP12. Arrowheads indicate binding of AfFKBP12 to CN at the hyphal septum (d F22T, e Q50M, f R55E, g F88H). The FK506-binding pocket of WT (blue surface) and the pocket resulting from the mutation (red surface) are shown. Mutation site is denoted with an “*” and shown in stick format (red bar in bar graph), while residues comprising the binding pocket are shown in orange lines (black bars in bar graph). The stability and quality of the simulation is shown in the Cα RMSD plot. h The all atom (top) and backbone (bottom) RMSD denoting the structural variation due to the mutation compared to the WT structure (5HWB). See also Supplementary Figs. 1 and 3