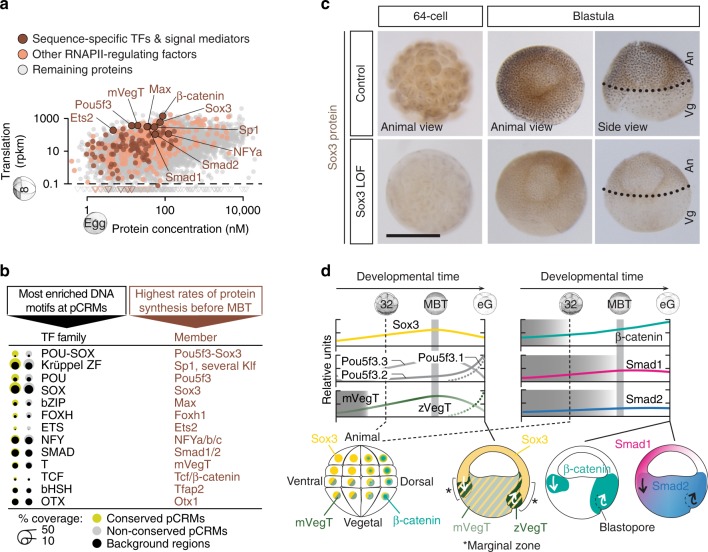
Fig. 2.
Search for ZGA-critical proteins based on their significantly enriched DNA recognition motifs at accessible and engaged (RNAPII+/H3K4me1+) pCRMs and their high translation frequency before the MBT. a Maternal protein concentrations in the egg13 versus ribosome footprint (translation) levels at the 8-cell stage14. Most frequently translated representatives of various TF families are labelled. b Matching canonical pCRM-enriched DNA motifs (sorted by statistical significance) with frequently translated TFs and signal mediators. c WMIHC of Sox3 protein in control and Sox3 loss-of-function (LOF) embryos at the 64-cell and blastula stage. Nuclear accumulation of Sox3 protein was detected in both the animal (An) and vegetal (Vg) hemisphere of control embryos. Scale bar, 0.5 mm. d Graphical illustration of protein levels (derived from mass spectrometry data42) and nuclear localisations (mainly derived from WMIHC, see references below) of selected TFs and signal mediators based on our and previously published results: Sox3 (this study and ref. 50), mPouV (Pou5f3.2 and Pou5f3.3) and (zygotic) Pou5f3.1 (deduced from transcript data15), mVegT and zVegT16, β-catenin10,17, Smad1 (this study and refs. 10,18) and Smad2 (this study and refs. 10,18). Shaded boxes indicate periods of non-nuclear protein localisation. Arrows indicate tissue movements of gastrulation. Abbreviations used for the developmental timeline: 8 and 32, 8-cell and 32-cell stage; MBT, mid-blastula transition; and eG, early gastrula stage