Fig. 1.
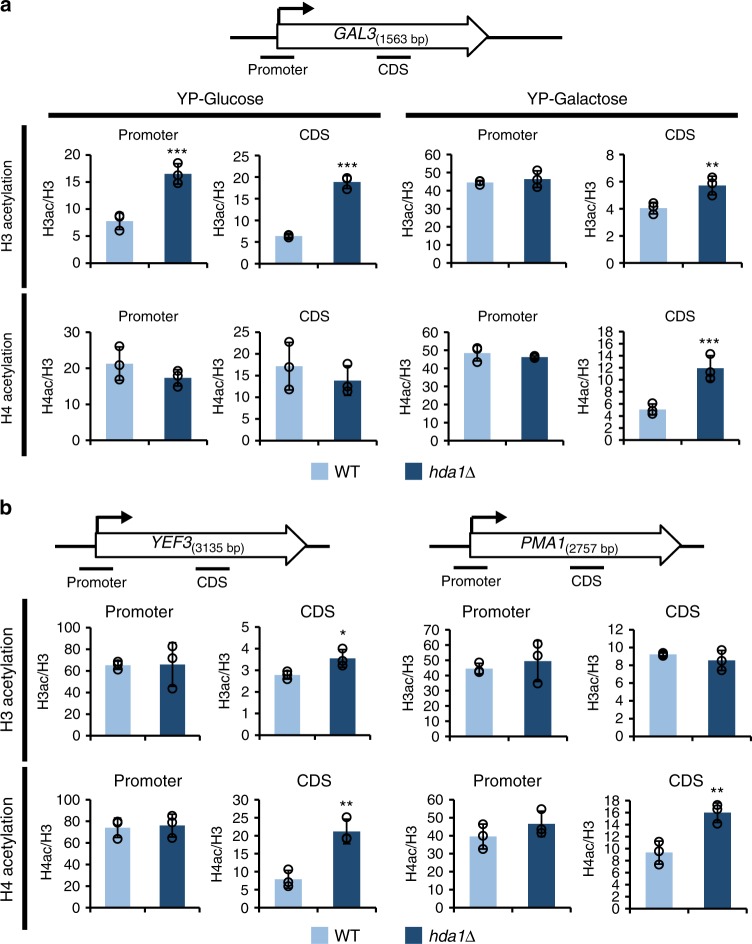
Hda1C preferentially deacetylates histone H4 at actively transcribed genes. a Hda1C specifically deacetylates histone H4 at active GAL3-coding regions. Crosslinked chromatin from the indicated strains grown in YP-Glucose (YPD) or YP-Galactose was precipitated with an anti-H3, anti-acetyl H3, or anti-acetyl H4 antibody as indicated. PCR analysis of the precipitated DNA was carried out on the promoter and coding regions of GAL3. A non-transcribed region located close to the telomere of chromosome VI was used as an internal control. The signals for acetyl H3 and acetyl H4 were quantitated and normalized to the total H3 signal. Error bars show the standard deviation calculated from three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t tests). b Hda1C deacetylates histone H4 at coding regions of the actively transcribed genes YEF3 and PMA1. Crosslinked chromatin from the indicated strains grown in YPD was precipitated with an anti-H3 or anti-acetyl H4 antibody as indicated, and a ChIP assay was performed as in a. Error bars show the standard deviation calculated from three biological replicates, each with three technical replicates. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t tests). Source data are provided as a Source Data file