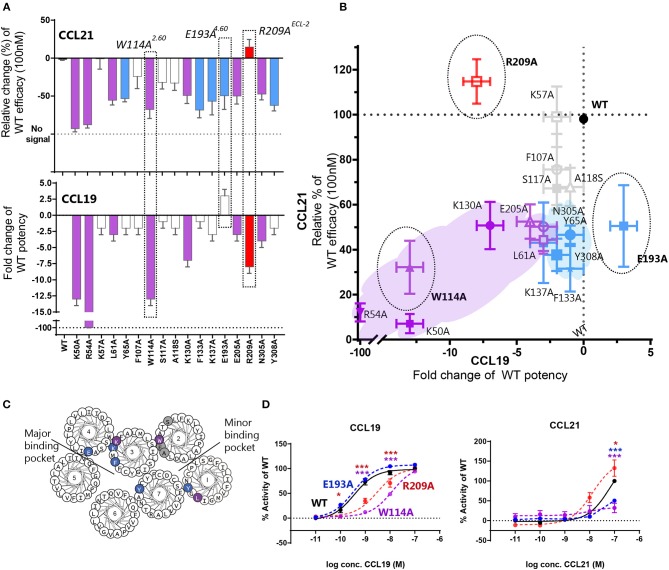
Figure 2.
Mutagenesis study of CCR7 showing changes of CCL21 and CCL19 G protein signaling by CCR7 mutations. (A) Barplot displaying change of CCL21- or CCL19-signaling by CCR7 mutations evaluated in a cAMP accumulation assay. Changes are displayed as relative change of efficacy at 100 nM CCL21, or fold change of potency for CCL19. Colors correspond to colors in (B), where purple identifies mutations impairing both ligands, blue refers to mutations only affecting CCL21, red refers to mutations only affecting CCL19, and gray identifies mutations with no impact. Three mutations are highlighted, which are also highlighted in (B) and presented with their dose-response curves in (D). (B) Scatterplot comparing the effect on CCL21 signaling to that of CCL19. Mutations are plotted with their values from (A) and colored according to the description in (A). (C) Helical wheel of CCR7 with mutations identified according to effect on CCR7 signaling in (A,B). (D) Dose-response curve of CCR7W114A, CCR7 E193A, CCR7 R209A, and CCR7WT stimulated with CCL21 or CCL19 in a cAMP accumulation assay. Significant differences between mutant and WT curve analyzed by two-way ANOVA are identified with colored asterisks corresponding to the color of the signaling curve. Data are represented as mean values (±SEM) of at least three independent experiments performed in duplicates. To compensate for inter-assay variations data have been normalized to wildtype within each separate experiment before the collection of data. The n value of independent experiments for each mutation can be found in Table 1.