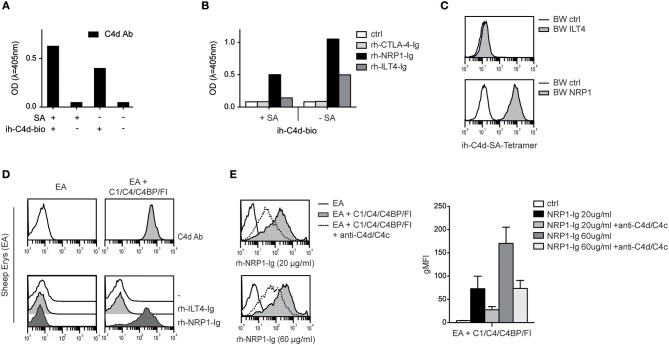
Figure 4.
Interaction between NRP1 and C4d deposited to surfaces via thioester binding following classical complement activation. (A) C4d biotinylated at its intrinsic thioester carbonyl via amine-PEG2-biotin reagent (ih-C4d-bio) was immobilized to a solid phase either via streptavidin (+SA) or in random orientation without SA (–SA) and detected by ELISA using a monoclonal C4d antibody. (B) Interaction between C4d, immobilized to a solid phase as shown in (A), and rh-NRP1-Ig and rh-ILT4-Ig. Rh-CTLA-4-Ig fusion proteins and goat anti-human-IgG (ctrl) served as negative controls. (C) C4d biotinylated via its intrinsic thioester was tetramerized using streptavidin-APC and probed with BW cells expressing ILT4 or NRP1 and analyzed via flow cytometry. (D) Antibody-coated sheep erythrocytes (EA) bearing C4d were prepared using purified C1, C4, C4 binding protein (C4BP), and factor I (FI) as described in Material and Methods. Deposition of C4d was detected with a monoclonal C4d antibody (upper panel). Interaction between C4d-loaded EA and control EA with immunoglobulin fusion proteins (rh-ILT4-Ig; rh-NRP1-Ig) is shown in the lower panel. (E) Binding of goat anti-human-IgG (ctrl) or rh-NRP1-Ig (20 or 60 μg/ml) to C4d-EA in the presence or absence of an anti-C4d and anti-C4c antibodies. Data shown are representative for two independently performed experiments. gMFI, geometric mean of fluorescence intensity.