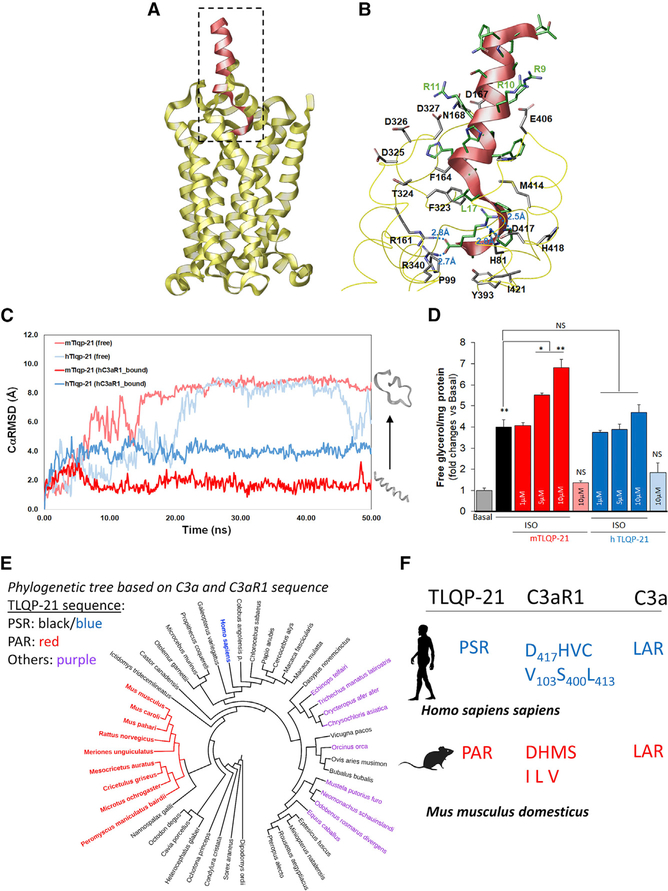
Figure 4. Homology Modeling and Biological Significance of TLQP-21/C3aR1 in Humans.
(A) Homology modeling of hC3aR1 (yellow ribbon) with bound mTLQP-21 (red ribbon).
(B) Binding site of hC3aR1 (labeled in black) with bound mTLQP-21 (labeled in green) after 50 ns simulation showed that TLQP-21 R21 forms multiple salt bridges with nearby R161, R340, and D417. mTLQP-21 containing the conserved RRRH motif was found to be surrounded by D167, D325, D326, D327, and E406, which could stabilize the α helix portion of TLQP-21 upon C3aR1 binding.
(C) Molecular dynamics simulation of TLQP-21 (mouse [m], human [h]) in water and in complex with hC3aR1. The CαRMSDs are shown for unbound mTLQP-21 (salmon) and unbound hC3aR1 (light blue), hC3aR1 (gray and black), mTLQP-21-bound hC3aR1 (red), and hTLQP-21-bound hC3aR1 (blue). The simulation showed that mTLQP-21 binding to hC3aR1 retained its secondary helical structure compared with the partially unfolded hTLQP-21 bound to hC3aR1 and the completely unfolded m/hTLQP-21 in water.
(D) mTLQP-21 potentiates ISO (10 nM)-induced lipolysis in human adipocytes (F(9,23) = 59.4, p < 0.0001). **p < 0.00.
(E) Phylogenetic analysis of the combined C3a and C3aR1 sequence of the 87 species for which the three proteins (VGF, C3, and C3aR1) are present in NCBI. The color highlights the sequence at the C terminus of TLQP-21. Red, PAR; black (blue for humans), PSR; purple, other sequences (full details are presented in Table S3). The specific Murinae and Cricetinae subfamilies have the exclusive invariant PAR motif in TLQP-21. The phylogenetic tree was built using the Itol software (https://itol.embl.de).
(F) Diagrams of critical motifs in humans and mice. The silhouettes of Homo sapiens and Mus musculus are from http://www.phylopic.org. Data are expressed as average and SEM.
See also Figures S5–S7 and Table S3.