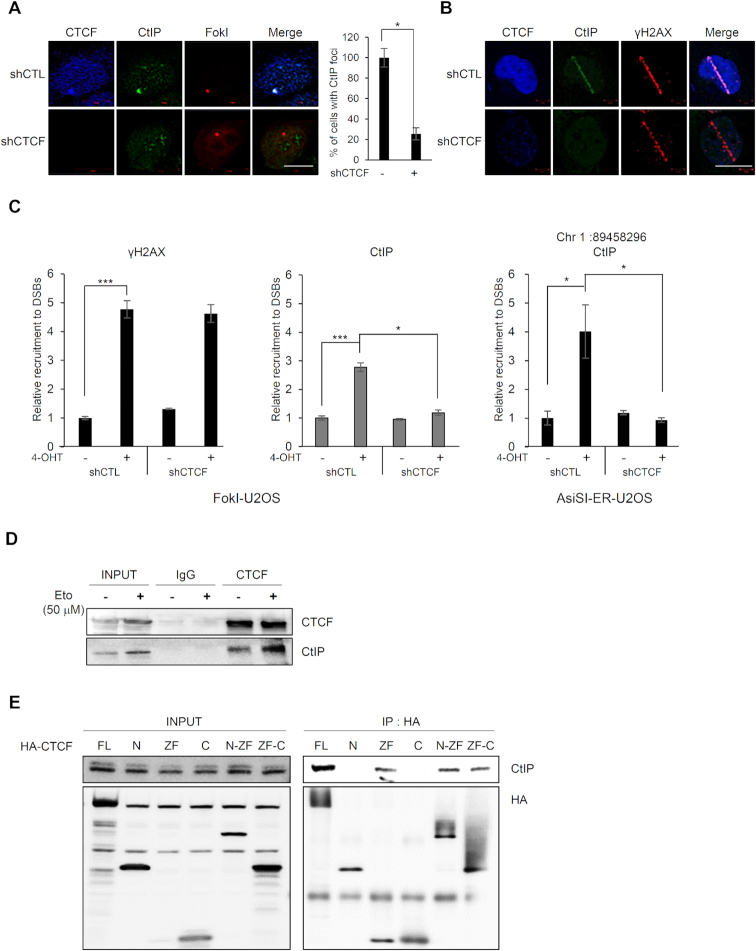
Figure 4.
CTCF is required for CtIP recruitment at DNA lesions. (A) Immunofluorescence was performed 4 h after induction of double-strand breaks (DSBs) by mCherry-LacI-FokI in CTCF-depleted (shCTCF) or control (shCTL) FokI-U2OS cells; scale bar: 10 μm. Bar graph represents the percentage of cells with CtIP (green) that co-localized at mCherry-FokI (red) foci. Data are the means ± SD of at least three independent experiments. More than 100 cells were counted in each experiment; *P≤ 0.05. (B) CTCF-depleted (shCTCF) or control (shCTL) U2OS cells were subjected to laser micro-irradiation. Cells were fixed and stained with the indicated antibodies. The scale bar represents 10 μm. (C) ChIP-qPCR was performed with an antibody to CtIP and γ-H2AX in the CTCF-depleted (shCTCF) or control (shCTL) FokI-U2OS cells (left) and AsiSI-ER-U2OS cells (right), with (+) or without (−) induction of DSBs. The fold enrichment values were relative to those of cells without induction of DSBs. Data are means ± SD of at least three independent experiments, and all qPCR reactions were performed in triplicate; *P≤ 0.05; ***P≤ 0.001. (D) CTCF interacts with CtIP. Co-immunoprecipitation assays were performed using control IgG and anti-CTCF with (+) or without (−) etoposide (Eto) treatment, and the immunoprecipitates were probed for the indicated proteins by western blotting (IB). (E) CTCF interacts with CtIP via its zinc finger domain. HA-tagged full-length CTCF and its truncated fragments (see Figure 1D, top) were expressed in 293T cells. HA-immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and blots were probed for HA (bottom) and CtIP (top).