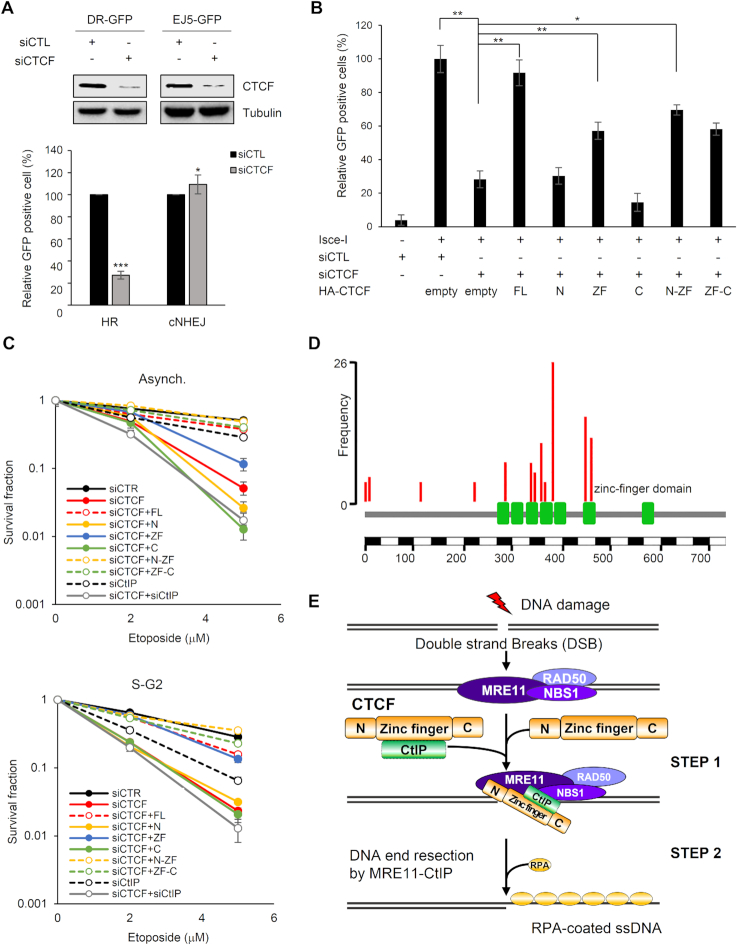
Figure 7.
CTCF–CtIP interaction contributes to CTCF-mediated homologous recombination (HR) and survival upon exposure to DNA damage. (A) U2OS-based homologous recombination- (DR-GFP) or canonical non-homologous end joining- (EJ5-GFP) reporter cell lines were co-transfected with siRNA (control, siCTL, or endogenous CTCF-specific, siCTCF) and I-SceI as indicated. Homologous recombination (HR) and canonical non-homologous end joining (cNHEJ) efficiencies were analyzed as in part (A). The plotted values are means ± SEM from at least three independent experiments; *P≤ 0.05; ***P≤ 0.001. (B) HR reporter cells (DR-GFP) were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and HA-tagged CTCF constructs together with I-SceI and subjected to an HR assay as in part (A) (see Supplementary Figure S13C indicating knockdown of endogenous CTCF and supplementation with the full-length or truncated constructs of CTCF.) The plotted values are means ± SEM from at least three independent experiments; *P≤ 0.05; **P≤ 0.01. (C) Effect of ectopic expression of the indicated HA-tagged CTCF proteins on survival of CTCF-depleted HeLa cells after treatment with etoposide. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and HA-tagged CTCF constructs. The cells in asynchronous or S/G2 phase were treated with etoposide, and survival fractions were confirmed by a clonogenic survival assay. The intensities and areas of the colonies were measured using ImageJ software (see Supplementary Figure S13D showing depletion of CTCF or CtIP and supplemented CTCF protein levels.). (D) Somatic point mutations (nonsense and missense) of CTCF from Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer (COSMIC) as of 13 October, 2018. Among them, 14 substitution mutations were identified in ≥4 samples across tumors in the COSMIC database. Eight out of the 14 mutations were located on the zinc finger (ZF) domain, which was defined as Pfam (ID P49711). As the frequency of mutations in the ZF domain of CTCF was higher than that in its N-terminal domain, the somatic mutations were significantly enriched within the ZF domain in cancer. (E) Model for the role of CTCF in DNA end resection of HR-mediated repair via CtIP recruitment. The MRN complex recognizes and binds to double-strand breaks (DSBs) and recruits CTCF to sites of DNA damage. In turn, CTCF promotes the recruitment of CtIP to DSBs and enhances DNA end resection.