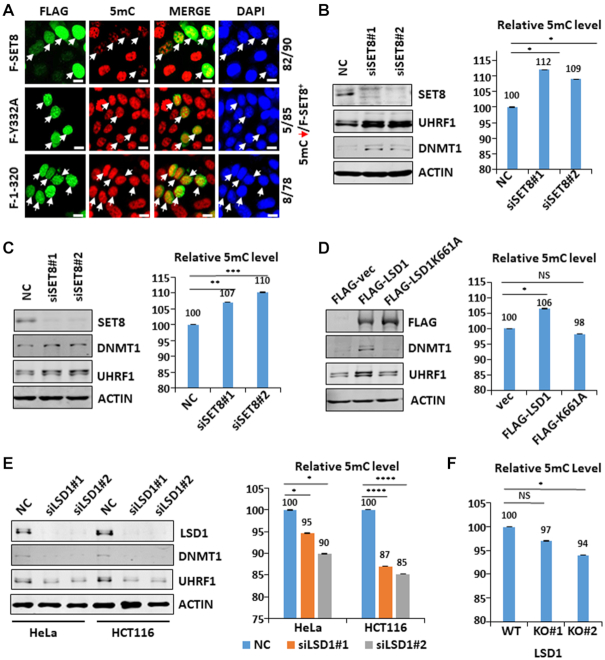
Figure 6.
Both SET8 and LSD1 play a role in control of global DNA methylation. (A) Immunostaining assay using anti-5mC antibody showing that ectopic overexpression of SET8 impaired the global level of DNA methylation in a methylase activity-dependent manner. (B) Quantitative HPLC analysis showing that knockdown of SET8 in HEK293T cells resulted in elevated global levels of DNA methylation (right panel). Western blot analysis in the left panel validated that knockdown of SET8 resulted in elevated levels of UHRF1 and DNMT1 proteins. *P< 0.05. (C) Quantitative HPLC analysis showing that knockdown of SET8 in HeLa cells resulted in elevated global levels of DNA methylation (right panel). Western blot analysis in the left panel showing that knockdown of SET8 resulted in elevated levels of UHRF1 and DNMT1 proteins. **P< 0.01; ***P< 0.001. (D) Quantitative HPLC analysis showing that ectopic overexpression of LSD1 but not its demethylase inactive mutant in HEK293T cells resulted in elevated global levels of DNA methylation (right panel). Western blot analysis in the left panel showing that ectopic overexpression of LSD1 but not its mutant elevated the levels of UHRF1 and DNMT1 proteins. *P< 0.05. (E) Quantitative HPLC analysis showing that knockdown of LSD1 in HeLa and HCT116 cells resulted in substantial reduction of global DNA methylation (right panel). Western blot analysis in the left panel validated that knockdown of LSD1 resulted in substantial reduction of both UHRF1 and DNMT1 proteins. *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01; ***P< 0.001. (F) Quantitative HPLC analysis showing reduced global levels of DNA methylation in LSD1 knockout HeLa cell lines. *P< 0.05.