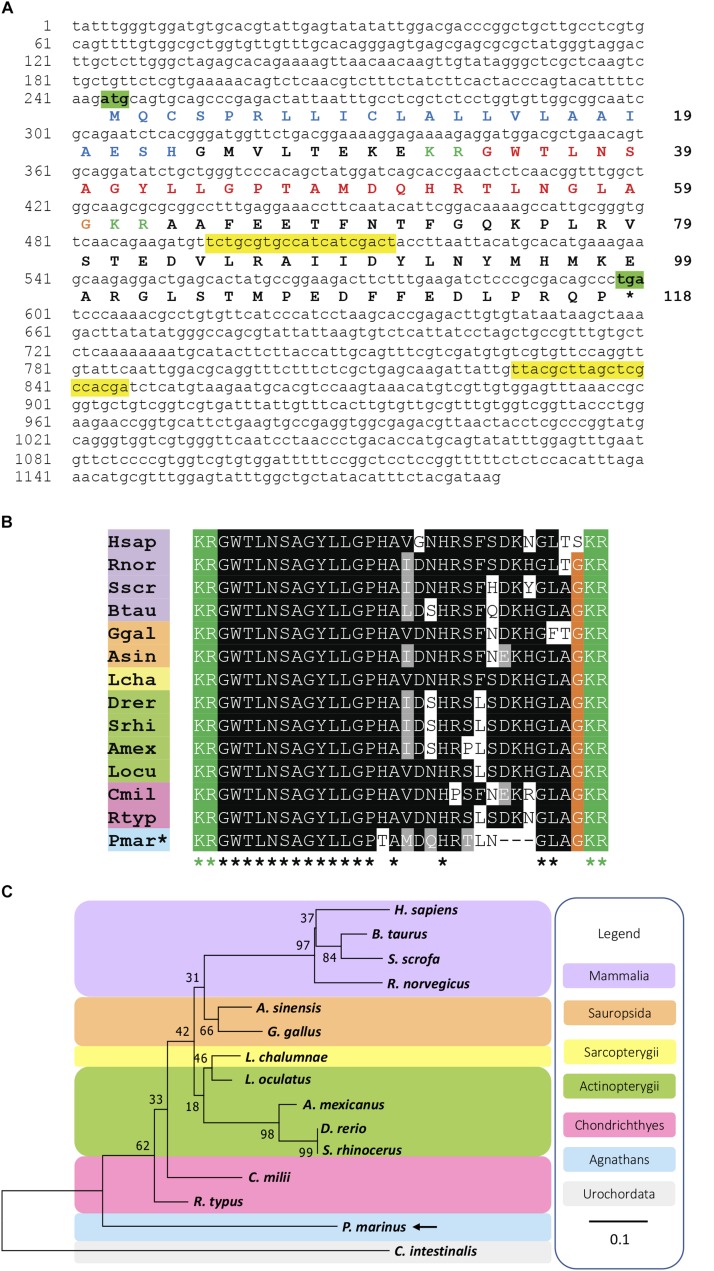
FIGURE 1.
Identification of a galanin precursor in the sea lamprey Petromyzon marinus. (A) Nucleotide sequence (lower case) of a transcript that encodes the Petromyzon marinus galanin precursor (PmGalP; upper case). The start and stop codons are highlighted in green. The predicted signal peptide sequence is shown in blue and dibasic cleavage sites are shown in green. The putative galanin peptide derived from the precursor protein is shown in red, with the C-terminal glycine that is substrate for amidation shown in orange. The primers used for cloning of a fragment of PmGalP cDNA are highlighted in yellow. (B) Alignment of a region of PmGalP, including the galanin peptide bounded by dibasic cleavage sites, with the corresponding region of galanin precursor proteins from other vertebrate species. Conserved residues are highlighted, with conservation in more than 70% of sequences shown in black and with conservative substitutions shown in gray. (C) Neighbor-joining tree showing relationships of galanin-type precursors in selected chordate species. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The analysis was conducted in MEGA 7. The urochordate galanin-like sequence from Ciona intestinalis (Cint) was used to root the tree and is highlighted in gray. Species names in the alignment (B) are as follows: Hsap (Homo sapiens), Btau (Bos taurus), Rnor (Rattus norvegicus), Sscr (Sus scrofa), Ggal (Gallus gallus), Asin (Alligator sinensis), Lcha (Latimeria chalumnae), Srhi (Sinocyclocheilus rhinocerous), Drer (Danio rerio), Amex (Astyanax mexicanus), Locu (Lepisosteus oculatus), Rtyp (Rhincodon typus), Cmil (Callorhinchus milii), Pmar (Petromyzon marinus). Additionally, in the alignment (B) and the phylogenetic tree (C), species names are highlighted in taxon-specific colors: purple (mammals), orange (sauropsids), yellow (lobe-finned fishes), green (ray-finned fishes), pink (cartilaginous fishes), blue (agnathans). The accession numbers and the alignment of the sequences used to build this phylogenetic tree are shown in Supplementary File S1.