Fig. 2. Experimental setup.
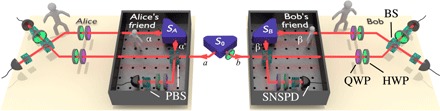
Pairs of entangled photons from the source S0, in modes a and b, respectively, are distributed to Alice’s and Bob’s friend, who locally measure their respective photon in the {∣h〉, ∣v〉}-basis using entangled sources SA, SB and type I fusion gates. These use nonclassical interference on a polarizing beam splitter (PBS) together with a set of half-wave (HWP) and quarter-wave plates (QWP). The photons in modes α′ and β′ are detected using superconducting nanowire single-photon detectors (SNSPDs) to herald the successful measurement, while the photons in modes α and β record the friends’ measurement results. Alice (Bob) then either performs a Bell-state measurement via nonclassical interference on a 50/50 beam splitter (BS) on modes a and α (b and β) to measure A1 (B1) and establish her (his) own fact or removes the BS to measure A0 (B0) to infer the fact recorded by their respective friend (see the Supplementary Materials for details).
