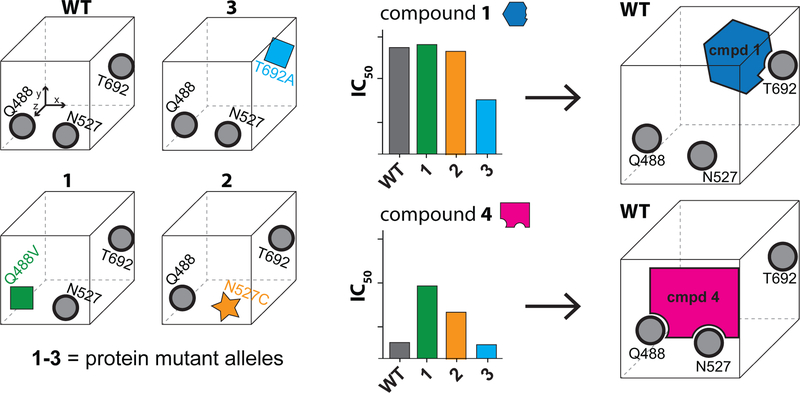
Figure 6. Developing compound-target binding models using the RADD approach.
Schematic for the RADD approach. Mutations that maintain biochemical activity (e.g. ATPase) but alter the shape and electrostatics of the inhibitor binding site are identified (left). Analyses of inhibitor activity against the different mutant alleles reveal key inhibitor-protein contacts (middle) and guide the selection of robust binding models (right).