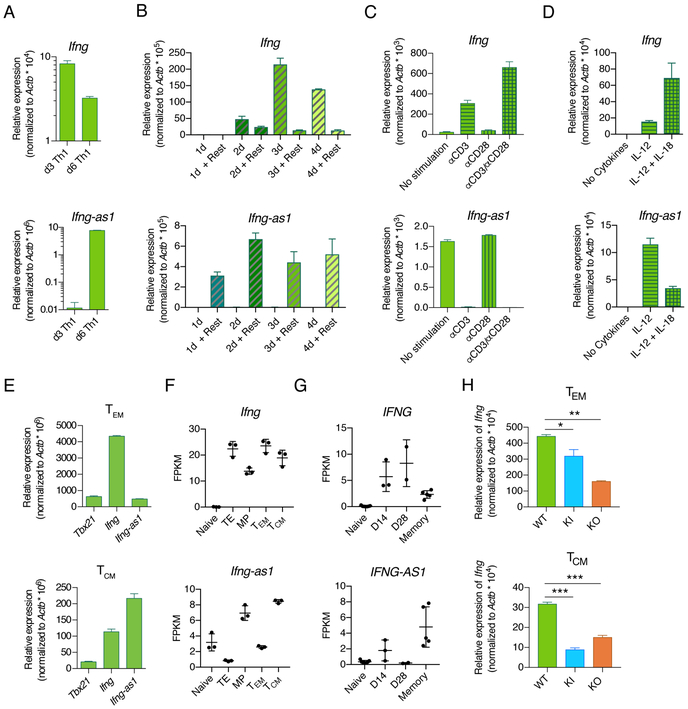
Figure 6: Ifng-as1 expression is suppressed by TCR stimulation but maintained in long-lived memory cells in the absence of antigen stimulation.
(A)-(D) Naïve T cells from WT mice were isolated by FACS and cultured under Th1 polarization conditions for up to 6 days. Ifng and Ifng-as1 expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR and normalized to the expression of β-actin. Shown are representative graphs from n=2 independent experiments. Graphs show mean ± sem. (A) Ifng and Ifng-as1 expression on day 3 and on day 6 of culture. (B) αCD3/αCD28 stimulation was withdrawn at different time points of culture, followed by 24 hours of resting. Expression of Ifng (top panel) and Ifng-as1 (bottom panel) for indicated conditions was analyzed by RT-qPCR and normalized to the expression of β-actin. (C) Cells were stimulated under Th1 polarizing conditions for 2 days. Afterwards cells were cultured in IL-12-containing medium in the presence or absence of αCD3 or αCD28 stimulation for an additional period of 24 hours. (D) Cells were stimulated without cytokines or in the presence of IL-12 or IL-12 and IL-18 for 6 days. (E) Effector memory cells (TEM, CD4+CD25−CD44+CD62L−) or central memory cells (TCM, CD4+CD25−CD44+CD62L+) were isolated from WT mice. Tbx21, Ifng, and Ifng-as1 expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR and normalized to the expression of β-actin. Shown are representative data from n=3 independent experiments. Graphs show mean ± sem. (F) CD45.1+CD45.2− P14 cells (LCMV-gp33 specific transgenic TCR, CD45.1+) were injected intravenously into CD45.2+ WT mice. The next day, these mice were challenged with 2 × 105 pfu of LCMV Armstrong. At day 8, terminal effector cells (CD8+CD45.1+KLRB1+CD127−) and memory precursor cells (CD8+CD45.1+KLRB1− CD127+) were isolated from spleens using FACS. Effector memory cells (CD45.1+CD44+CD127+CD62L−) and central memory cells (CD45.1+CD44+CD127+CD62L+) were collected by FACS from CD8+ T cell enriched splenocytes 48 days after infection from splenic CD8+ fractions. Naïve cells (CD8+CD44−CD62L+) were independently collected from the spleens LCMV-naive CD45.1+CD45.2− P14 mice. Ifng and Ifng-as1 expression was analyzed by RNA sequencing. (G) Expression of IFNG and IFNG-AS1 in naive and A2-NS4B214 tetramer+ effector (day 14, day 28) and long-term memory CD8+ T cells in human samples (see PMID: 29236685 for further details). (H) Ifng and Ifng-as1 expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR in effector memory cells (TEM, CD4+CD25−CD44+CD62L−) and central memory cells (TCM, CD4+CD25−CD44+CD62L+) from WT mice, Ifng-as1 KO mice, and Ifng-as1-PolyA KI mice. Shown are representative graphs from n=3 independent experiments. Graphs show mean ± sem. *p<0.05 **p<0.01 ***p<0.001.