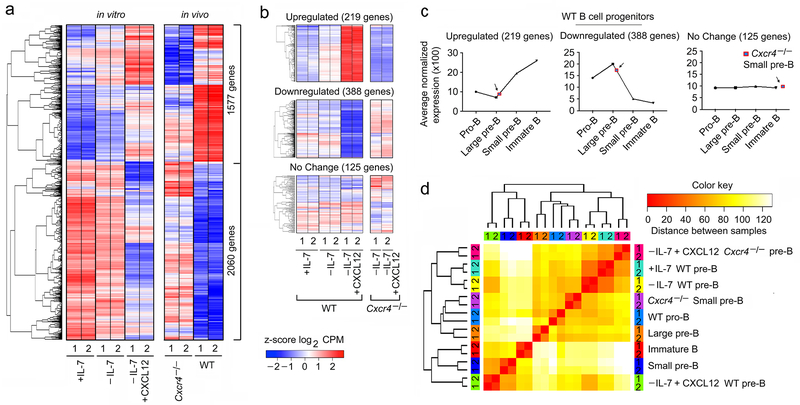
Figure 5. CXCR4 signaling determines small pre-B cell identity.
a, Hierarchical clustering of differentially regulated genes (RNA-Seq) identified at q<0.05 in WT pre-B cells, cultured as indicated compared to flow-purified Cxcr4fl/fl-mb1-cre+/− (Cxcr4−/−) and WT small pre-B cells (q<0.05). Common differentially expressed genes (both in in vitro and in vivo) were plotted in same order. b, Heat map of differentially regulated genes in vitro that changed by at least two-fold, were highly expressed (at least 1/10th of B2m expression), and in which differential regulation was statistically robust (P<10−5). Upregulated, downregulated and representative unchanged genes from indicated culture conditions were presented in the top, middle and bottom panels respectively. c, Average expression of the same upregulated (top panel), downregulated (middle panel) and unchanged genes (bottom panel) in different in vivo WT B cell progenitors indicated. d, Comparison of transcriptional programs regulated by CXCR4 both in in vivo and in vitro based on the expression levels of the 3637 genes that were differentially expressed under any condition. Hierarchical clustering was run on z-scored Log2 normalized expression levels, using a Euclidian correlation distance metric. The clustering dendrogram was plotted against the distance matrix for all indicated samples.