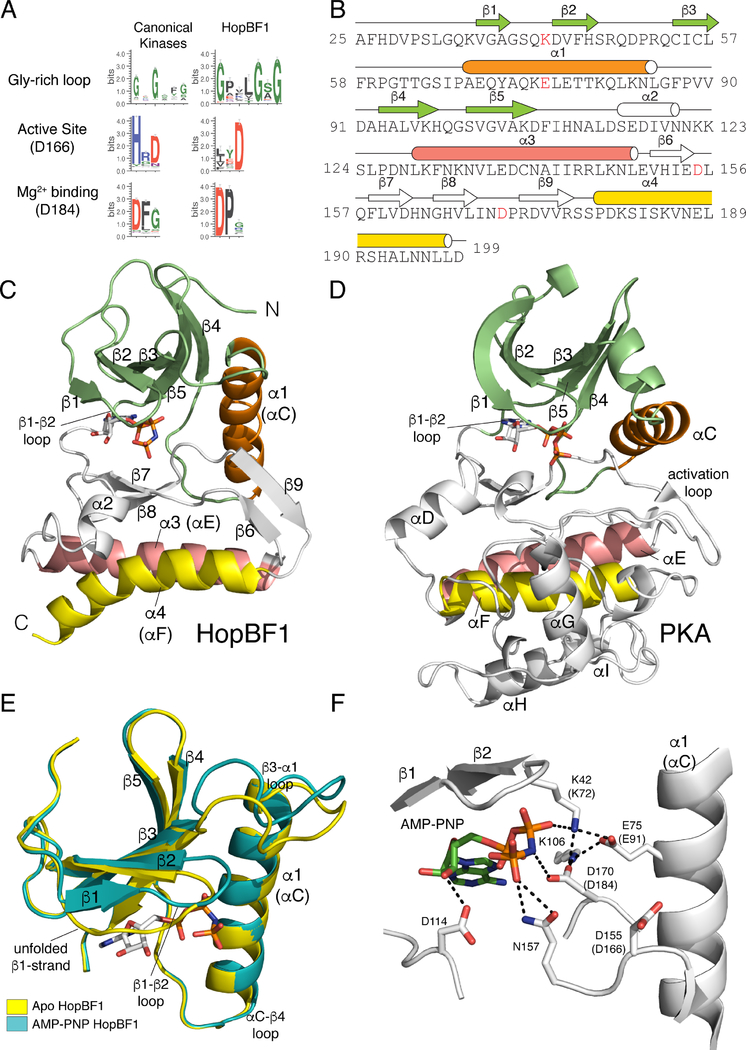
Figure 1. HopBF1 adopts a minimal protein kinase fold (Related to Figure S1).
(A) Sequence logo analysis of 161 HopBF1 homologs depicting the conservation of predicted active site residues. The Gly-rich loop (β1-β2 loop) and the active site HRD (PKA, D166) and DFG (PKA, D184) are shown.
(B) Amino acid sequence of E. americana HopBF1 depicting the secondary structural elements. The N-lobe β-strands are in lime, the α1 (PKA αC equivalent) helix is in orange, the C-lobe β-strands and the α2 helix are in white, the α3 helix (PKA αE) is in salmon and the α4 helix (PKA αF) is in yellow. E. americana HopBF1 contains 203 amino acids.
(C) Ribbon representation of E. americana HopBF1. Color coding as in Figure 1B.
(D) Ribbon representation of PKA (PDB code 1ATP). Color coding as in Figure 1B. The GHI helical subdomain, which is missing in HopBF1, is in white.
(E) Superposition of the N-lobes of the Apo and AMP-PNP bound HopBF1 structures depicting the unfolded β1-strand in the Apo structure. The Apo structure is in yellow and the AMP-PNP bound structure is in teal.
(F) Enlarged image of the nucleotide-binding pocket showing the detailed molecular interactions involved in nucleotide binding. Active site residues are numbered and the PKA equivalent residues are shown in parentheses. The AMP-PNP molecule is also shown.