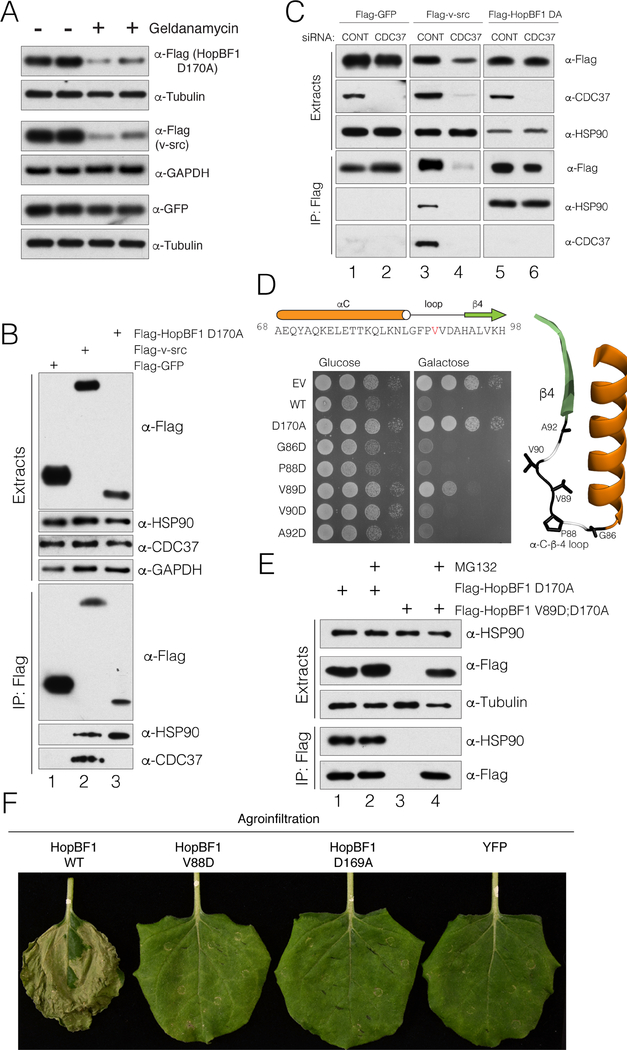
Figure 6. HopBF1 mimics an HSP90 client (Related to Figure S6).
(A) Protein immunoblotting of HEK293A cell extracts depicting the levels of E. americana Flag-HopBF1 D170A (upper), the HSP90 kinase client Flag-v-src (positive control; middle) and GFP (negative control; lower). Tubulin and GAPDH are used as loading controls.
(B) Protein immunoblotting of anti-Flag immunoprecipitates from HEK293A cell extracts expressing Flag-tagged GFP (Flag-GFP), v-src (Flag v-src) or E. americana HopBF1 D170A (Flag HopBF1 D170A). Immunoprecipitates and cell extracts were analyzed for HSP90 and CDC37. Cell extracts were also analyzed for HSP90, CDC37 and GAPDH as a loading control.
(C) Protein immunoblotting of anti-Flag immunoprecipitates from HEK293A cell extracts expressing Flag-tagged GFP (Flag-GFP), v-src (Flag v-src) or E. americana HopBF1 D170A (Flag HopBF1 DA) following depletion of CDC37 using siRNA. Immunoprecipitates and cell extracts were also analyzed for HSP90 and CDC37.
(D) Spot assay depicting the growth of S. cerevisiae expressing Flag-tagged E. americana HopBF1, the inactive D170A mutant or mutations within the αC-β4 loop. The primary and secondary structure of the αC-β4 loop is shown above and the structure of this region is shown on right in ribbon representation highlighting the mutated residues.
(E) Protein immunoblotting of anti-Flag immunoprecipitates from HEK293A cell extracts expressing Flag-tagged E. americana HopBF1 D170A (Flag-HopBF1 D170A) and the V89D; D170A mutant (Flag HopBF1 V89D; D170A). Cells were also pretreated with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 to prevent degradation of unfolded proteins.
(F) Photographs depicting leaves of N. benthamiana plants infiltrated with A. tumefaciens carrying WT HopBF1 or the indicated mutants V88D and D169A or YFP as a control. Photos were taken 7 days post infiltration.