Figure 6. RPA protects single strand DNA from A3A-medited cytosine deamination.
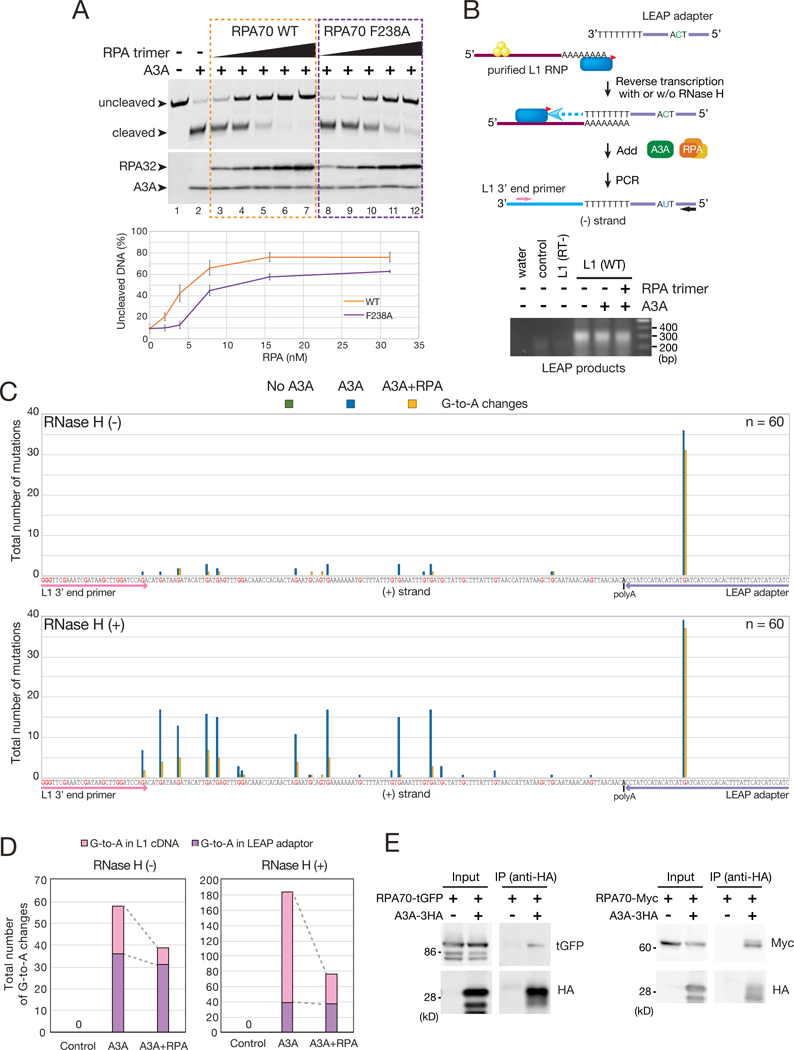
(A) RPA suppresses A3A-mediated deamination. Top: a single-strand LEAP adapter oligonucleotide (TM165) was incubated with His-A3A in the absence or presence of the WT RPA trimer or a mutant RPA trimer containing a F238A RPA70 subunit at concentrations ranging from 31.25 to 1.95 nM. Arrows indicate the uncleaved (no deamination) and cleaved (deamination) ssDNAs. A3A and RPA32 were detected by western blot. Bottom: quantification of non-deaminated ssDNA. X-axis, the RPA concentration. Y-axis, the percentage of uncleaved ssDNA. A reaction conducted in the absence of A3A and RPA (lane 1) was set to 100% uncleaved ssDNA. Error bars represent the standard errors calculated from three independent experiments.
(B) Rationale of the LEAP Assay. Top: The yellow circles and blue oval with the red triangle indicate ORF1p and ORF2p-3FLAG, respectively. The pink and black arrows indicate primers, which are specific to the engineered L1 expression vector (TM160) and the LEAP adapter (TM159), respectively. These primers were used to PCR amplify L1 cDNAs. Bottom: LEAP assays were conducted with purified L1 RNPs in the absence or presence of A3A and/or RPA. The representative image was obtained after PCR amplification of the LEAP products in the presence of RNase H. L1 RNPs isolated from cells transfected with pJM101/L1.3 (control) or pTMF3D702A (RT-) served as negative controls.
(C) Sequence analysis of LEAP products in the absence (top) or presence (bottom) of RNase H. Reactions were conducted in the absence of A3A (green), the presence of A3A (blue), or the presence of A3A and RPA (yellow). X-axis, the (+) strand L1 cDNA LEAP sequence. Guanine nucleotides are shown in red. Sequences underlined with pink and purple denote the L1 3’ end primer (TM160) and LEAP adapter (TM158), respectively. Outlined “A”, the position of the variably sized poly(A) tract. Y-axis, total number of G-to-A mutations. Non-A3A-mediated mutations are shown in Figure S6D.
(D) Distribution of A3A-mediated mutations in LEAP products in the absence or presence of RNase H. X-axis, LEAP reaction condition. Y-axis, total number of G-to-A mutations on the (+) strand L1 cDNA (pink) and LEAP adapter (purple).
(E) RPA association with A3A. HEK293T cells were transfected with A3A-3HA and either the RPA70-turboGFP (tGFP) or RPA70-Myc expression plasmids. A3A-3HA was immunoprecipitated using an anti-HA antibody; associated proteins were examined by western blot. HEK293T cells transfected with pcDNA3.1(+), instead of A3A-3HA, served as a negative control.
