Fig. 1.
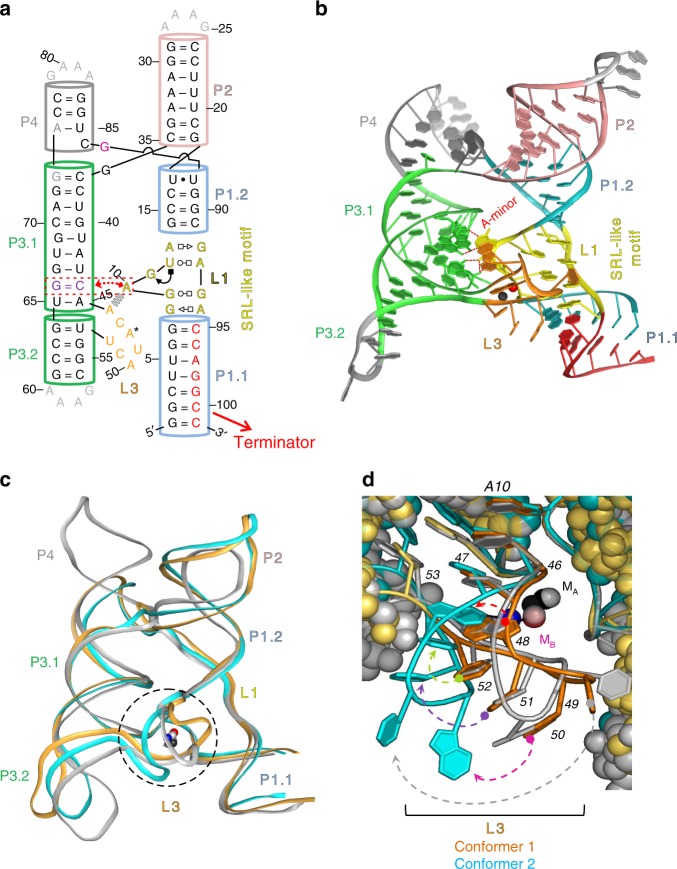
Sequence and structure of the X. oryzae (Xory) crystal structure. a Secondary structure of the X. oryzae crystal construct. A native CA dinucleotide was omitted between G73–A74 for crystallization purposes only. The A-minor interaction between L1 and L3 and the SRL-like conformation of L1 is shown. b Crystal structure of Conformer 1 (PDB ID: 6N2V) with different secondary structures labeled. c Comparison of overall structures of Conformers 1 (orange) and 2 (cyan) and the previous Mn2+-bound L. lactis structure (gray). The two molecules in the asymmetric unit are overall fairly similar. However, they differ dramatically at the metal ion binding sites (dotted circle). d Conformer 1 (orange) is relatively similar to the L. lactis structure at the MB,Mn binding site. All the same metal ion contacts are made, although U49, away from the Mn2+ site, is shifted (gray dotted arrow). Conformer 2 (cyan) differs in that a metal ion is still bound at the MB,Mn site, but only half of the metal ion contacts are made, and the binding site A48 is flipped (red dotted arrow) to expose N1 rather than N7. U49 (gray arrow), A50 (magenta arrow), C51 (purple arrow), and U52 (green arrow) are all significantly shifted from the previously reported Mn-bound conformation