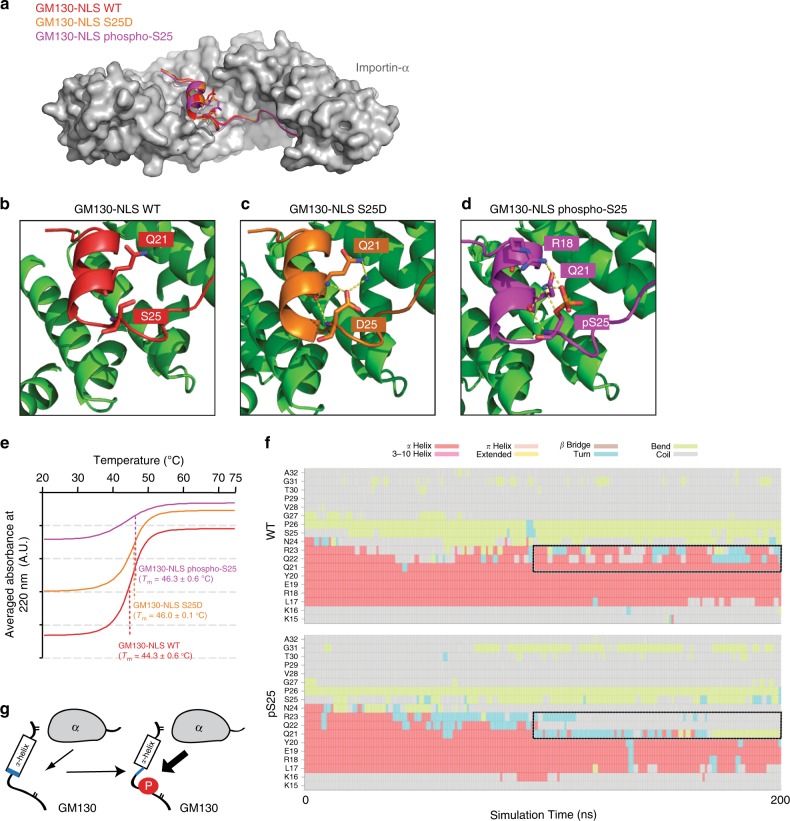
Fig. 2.
A phosphate moiety mediates GM130 intra-molecular interactions. a Superimposition of the GM130-NLS WT (red), GM130-NLS S25D (orange) and GM130-NLS phospho-S25 (purple) crystal structures. Importin-α (a.a. 70–498) is shown in gray. b–d Detailed views of the residue-residue interactions mediated by Serine-25 (b), Aspartic acid-25 (c), or Phosphoserine-25 (d) in GM130. Water molecules are shown as blue spheres. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by dotted lines. e Circular dichroism spectra of temperature scans at a wavelength of 222 nm for GM130-WT (red line), S25D (orange line) or phosphor-S25 (purple line) complexes. Each complex spectrum represents the average of three scans. The melting temperature (Tm) of each complex is indicated. f Mean secondary structure of GM130-NLS residues 15−32 (averaged over eight 200-ns simulations) in solution as a function of simulation time for native peptide (top) and phosphorylated peptide (bottom). g Schematic model of how phosphorylation on GM130-NLS disrupts the α-helix in apo state, enhancing Importin-α binding