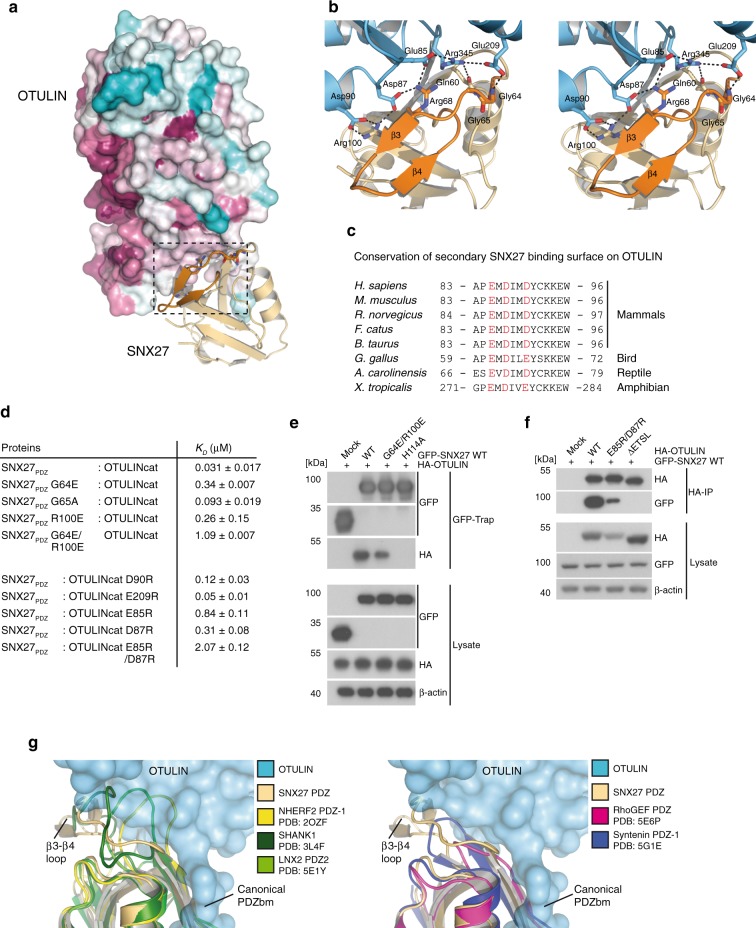
Fig. 4.
Secondary interface mediates high affinity interaction and selectivity between OTULIN and SNX27. a Surface representation of OTULIN colored based upon conservation calculated through the Consurf webserver. Box encloses the second SNX27 interface. b Close-up stereo view of the second interface of OTULIN from a. The unique β3–β4 hairpin insertion within the SNX27 PDZ domain is shown in orange. Hydrogen bonds between residues are shown with dotted lines. c Sequence alignment and conservation of second SNX27 binding surface in OTULIN orthologues from tetrapod animals. Conserved polar and electrostatic amino acids involved in binding to SNX27 are depicted in red. d Summary of SNX27–OTULIN affinities (KD) determined by ITC for mutations in the secondary interface. e HEK293 cells were co-transfected with HA-OTULIN and GFP-SNX27 WT or mutants that carry missense mutations in the canonical cargo binding site (H114A) or in the second OTULIN interface (G64E/R100E). Binding was analyzed after GFP-Traps by WB. f HEK293 cells were co-transfected with GFP-SNX27 and HA-OTULIN constructs. OTULIN mutants either lack the C-terminal PDZbm (ΔETSL) or carry missense mutations in the second SNX27 interface (E85R/D87R). SNX27 binding was analyzed after HA-IP by WB. g Superimposition of structurally related PDZ domains onto SNX27–OTULIN structure. All closely related PDZ domains lack the SNX27 β3-β4 hairpin insertion. PDZ domains of SHANK1, NHERF1, and LNX2 contain a larger insertion that may clash with the second interface on OTULIN (left). PDZs of RhoGEF and Syntenin1 contain a short loop at the equivalent position that would not clash with the second interface of OTULIN (right). Source data are provided as a Source Data file