Fig. 5.
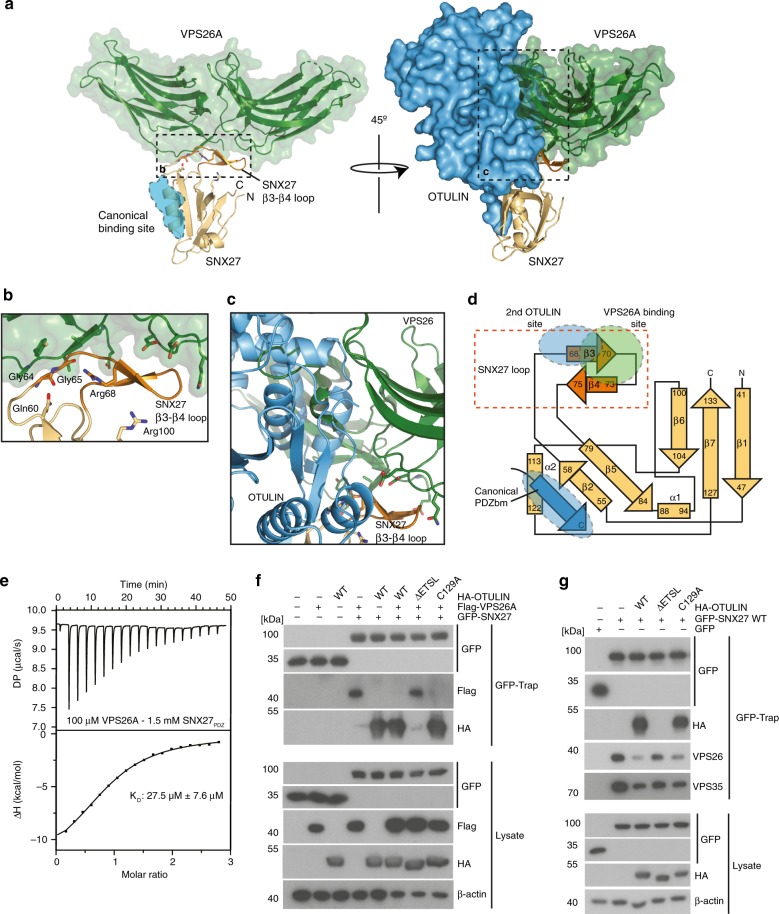
OTULIN competes with VPS26 for SNX27 binding. a SNX27 utilizes residues from the β3–β4 insertion to engage with the retromer complex. Structure of SNX27 bound to VPS26A (green surface) (PDB: 4P2A). The canonical PDZbm of OTULIN is shown as a blue cartoon. Rotation of the complex by 45° with superimposition of the OTULIN-SNX27 and VPS26A-SNX27 structures onto SNX27. b Close-up view of a, with residues from the SNX27 β3–β4 hairpin that bind to VPS26A shown. c Close-up view of a revealing extensive clashes between OTULIN and VPS26A through overlapping binding sites on the β3–β4 hairpin. d Topology diagram of SNX27 showing the canonical PDZbm binding site and the VPS26A and OTULIN binding sites on the β3–β4 hairpin. e ITC data for SNX27 PDZ domain titrated against VPS26A. f HEK293 cells were co-transfected with GFP-SNX27, Flag-VPS26A, and HA-OTULIN constructs as indicated. GFP-SNX27 was precipitated using GFP-Traps and tested for simultaneous interactions with VPS26A and OTULIN by WB. g HEK293 cells were co-transfected with GFP-SNX27 and HA-OTULIN constructs as indicated. Following GFP-Trap precipitation, binding of GFP-SNX27 to HA-OTULIN and effects on interaction of GFP-SNX27 with the endogenous retromer subunits VPS26 and VPS35 were monitored by WB. Source data are provided as a Source Data file