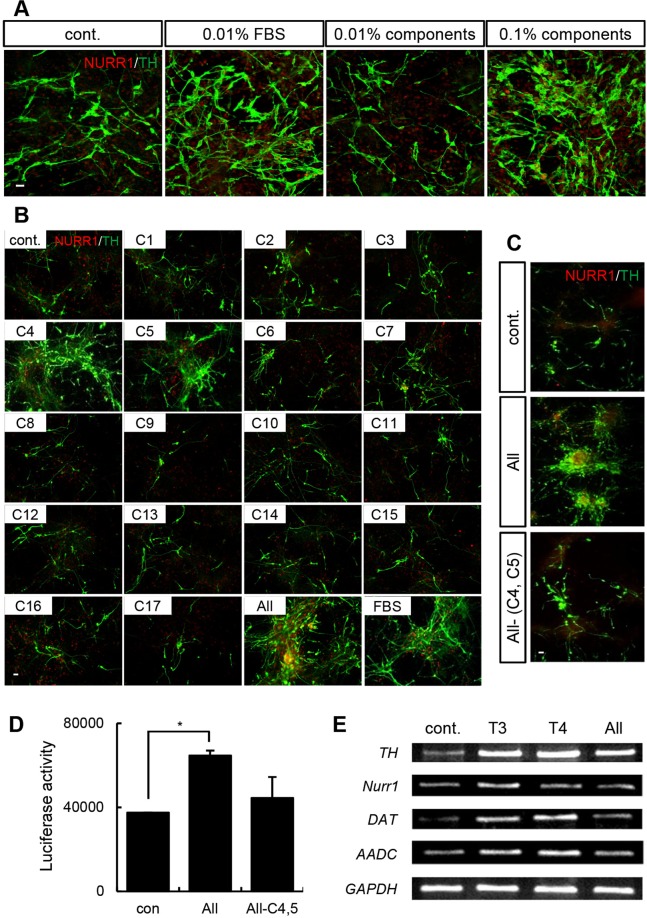
Figure 3.
T3 and T4 are key components of FBS required for DA neuron differentiation. (A) Immunocytochemistry showing that treatment with the chemical mixture increased the number of NURR1+ and TH+ DA neurons. The chemicals were diluted to a concentration equivalent to that found in FBS. The 0.1% chemical mixture had an effect similar to that of 0.01% FBS in Nurr1-overexpressing rat NPCs. (B) Cells were immunostained with anti-NURR1 and anti-TH antibodies on differentiation day 7. Untreated cells were used as the negative control, and cells treated with the chemical mixture containing the 17 components of FBS acted as the positive control. There were more TH+/NURR1+ cells upon treatment with candidate factors C4 and C5 exhibited than upon treatment with the other chemicals. (C) Cells treated without the candidate factors (C4: T3; C5: T4) were immunostained with anti-NURR1 and anti-TH antibodies on differentiation day 7. The number of DA neurons in the cultures decreased dramatically when C4 and C5 were eliminated. (D) A TH promoter assay in Nurr1-Mash1-overexpressing rat NPCs treated with the chemical mixture from which C4 and C5 were eliminated. (E) RNA was extracted from cells that were treated with T3 (50 pg/ml) or T4 (5 pg/ml) for 10 days. RT-PCR analysis was performed to examine the expression of DA neuron–related genes (Th, Nurr1, Dat, and Aadc). GAPDH expression was used as a loading control. The error bars are the S.E. *p < 0.05. Scale bar, 20 μm. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results.