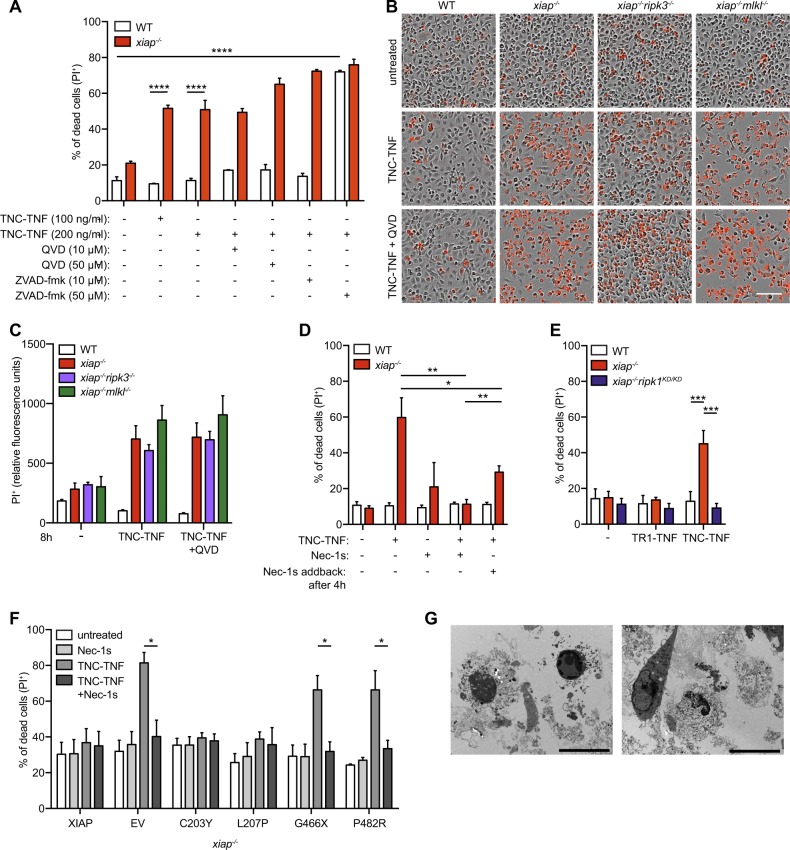
Fig. 3. RIPK1 kinase activity mediates TNFR2-induced cell death in xiap−/− macrophages, independent of apoptosis and necroptosis.
a WT or xiap−/− BMDMs were treated overnight with TNC-TNF in combination with either the caspase inhibitor QVD (10 or 50 μM) or ZVAD-fmk (10 or 50 μM). Cell death was measured via PI uptake by flow cytometry. b Representative phase-contrast images at 18 h after TNC-TNF and QVD (5 μM) stimulation in WT, xiap−/−, xiap−/−ripk3−/− and xiap−/−mlkl−/− BMDMs monitored for cell death by PI uptake using time-lapse photography. c PI+ BMDMs after 8 h stimulation with TNC-TNF and/or QVD using time-lapse photography. d BMDMs were treated with TNC-TNF in combination with the RIPK1 kinase inhibitor Necrostatin-1s (Nec-1s, 1 μM) or TNC-TNF pre-stimulation for 4 h and additional Nec-1s treatment. After 24 h cell death was measured by PI uptake and analysed by flow cytometry. e WT, xiap−/− or xiap−/−ripk1KD/KD BMDMs were treated with TNC-TNF and after 24 h analysed via PI uptake by flow cytometry. f Xiap−/− HoxB8 granulocytes were transfected with WT, XIAP or XIAP mutated constructs and stimulated with TNC-TNF or in combination with Nec-1s for 24 h. g Transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Xiap−/− BMDMs were treated for 12 h with TNC-TNF, fixed and prepared for analysis. Representative images are shown. Bars, 10 μm. a, c, d, e Data shown are mean ± SEM including n = 3–5 biological replicates. Experiments were repeated at least three times independently or (f) a minimum of three independent experiments, including triplicates for each experiment. Statistical significance was calculated using (a, c, d, e) two-way ANOVA or (f) Student t-test with *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001.