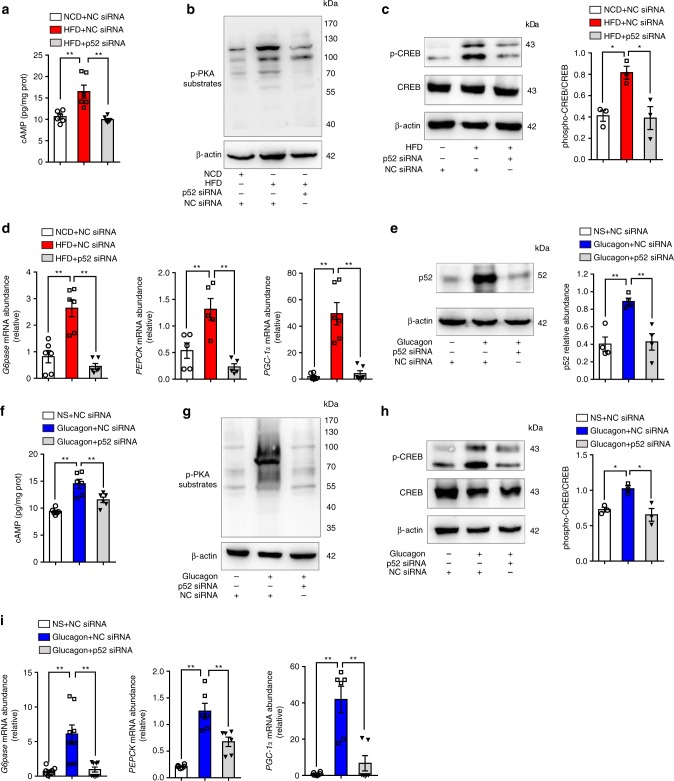
Fig. 2.
p52 knockdown blocks cAMP/PKA signaling. a Hepatic cAMP accumulation in the liver tissue of NCD-fed, HFD-fed, and HFD-fed mice with p52 silencing. Liver tissues were collected from the mice after 8 weeks feeding (n = 6). b, c Western blot analysis of phospho-PKA substrates (b) and p-CREB (c) expression in the liver tissue from the mice in panel a (n = 3). d qRT-PCR determination of mRNA levels of G6pase, PEPCK, and PGC-1α in the livers from the mice in panel a (n = 6). e Western blot analysis of p52 expression using lysates of the liver tissue from normal mice treated with glucagon (2 mg/kg body weight) and p52 siRNA or NC siRNA (n = 4). f Hepatic cAMP accumulation in the liver tissue of the mice (n = 6). g, h Hepatic phospho-PKA substrates and p-CREB protein levels in the mice (n = 3). i Hepatic mRNA levels of G6pase, PEPCK, and PGC-1α in the mice (n = 6). NCD normal chow diet, HFD high-fat diet, PKA protein kinase A, CREB cAMP-response element-binding protein, qRT-PCR quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, NS normal saline, G6pase glucose-6-phosphatase, PEPCK phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, PGC-1α peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha. Each bar represents mean ± SEM values. Statistical differences were determined by one-way ANOVA. *p < 0.05 vs. the control group, **p < 0.01 vs. the control group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file