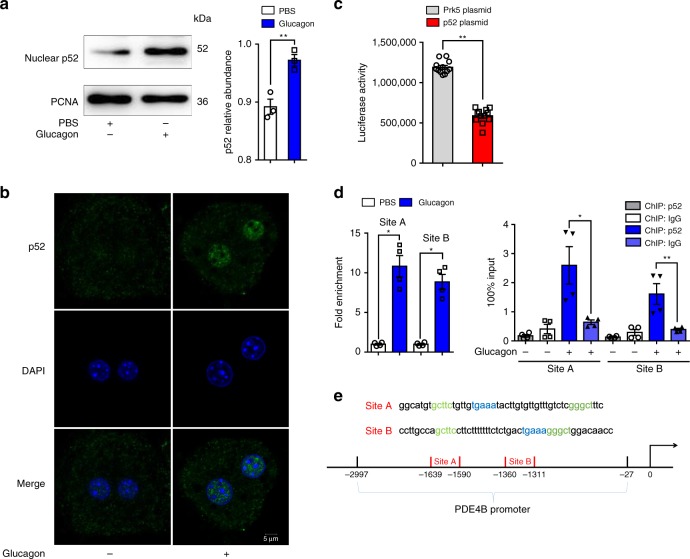
Fig. 4.
p52 binds to the PDE4B promoter and reduces its transcription. a The protein level of p52 in cell nuclei when exposed to glucagon (100 nM, 1 h). The PCNA level was used for normalization (n = 3). b Representative confocal images of primary hepatocytes exposed to glucagon (100 nM, 1 h). Scale bar represents 5 μm. c Luciferase reporter assay for inhibition effect of p52 on PDE4B gene promoter. The PDE4B luciferase reporter was co-transfected with p52 plasmid (1 µg) in 293 T cells. The luciferase activity was normalized with the internal control (Renilla luciferase, n = 12). d ChIP analysis to detect p52 binding to the PDE4B promoter. HepG2 cells were stimulated by glucagon for 1 h. Equal amounts of chromatin (DNA) were subjected to the ChIP assay with NF-κB2-specific antibody. Mice IgG and protein A/G beads alone were used as negative controls. p52 occupancy of the PDE4B promoter is shown relative to background signal with mice IgG control antibody. The ChIP analysis data are shown without normalization as 100% input (n = 4). e The probable p52-binding sites identified in the PDE4B promoter region. PBS phosphate buffer solution, PDE phosphodiesterase, PCNA proliferating cell nuclear antigen, DAPI 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical differences between pairs of groups were determined by a two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05 vs. control group, **p < 0.01 vs. control group. Source data are provided as a Source Data file