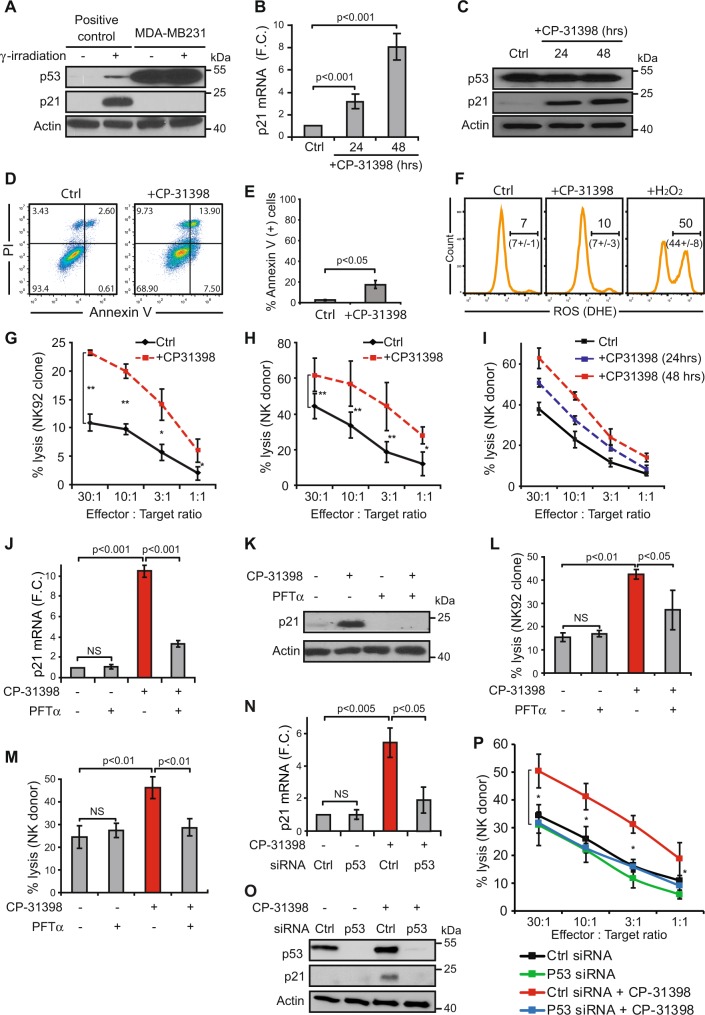
Fig. 1. The reactivation of p53 transcriptional activity by CP-31398 increases p53-mutated breast cancer cell susceptibility to NK-mediated lysis.
a MDA-MB231 cells express high level of mutated p53 (p53R280K) lacking transcriptional activity as shown by the absence of p53-dependent transactivation of its target gene p21 even after γ-irradiation. b, c 24-48 h treatment with CP-31398 reactivates p53 transcriptional activity in MDA-MB231 cells as shown by induction of p21 expression at both mRNA (b) and protein (c) levels. d–f CP-31398-induced apoptosis and ROS production were evaluated after 48 h treatment using AnnexinV/PI (d, e) or DHE (f) staining. g, h CP-31398 treatment (48 h) increases MDA-MB231 cell susceptibility to NK-mediated lysis. 51Cr release assay using NK92 (d) or NK cells isolated from a healthy donor (e) co-cultured with target cells at different E:T ratios are shown. i CP-31398 treatment increases MDA-MB231 cell susceptibility to NK-mediated lysis in a time dependent manner. A representative 51Cr release assay (from two independent experiments) using NK cells isolated from a healthy donor is shown. j, k PFT-α (an inhibitor of p53 transcriptional activity) inhibits CP-31398-dependent induction of p21 expression in MDA-MB231 cells at both mRNA (j) and protein (k) levels. l, m PFT-α inhibits the increase of MDA-MB231 lysis by NK cells observed when CP-31398 is used alone. 51Cr release assay using NK92 (l) or NK cells extracted from a healthy donor (m) co-cultured with target cells at the E:T ratio of 50:1 or 30:1, respectively, are shown. n–p The knockdown of mutated p53 expression using siRNA inhibits CP-31398-dependent induction of p21 expression in MDA-MB231 cells at both mRNA (n) and protein (o) levels and abrogate the CP-31398-dependent increase of MDA-MB231 lysis by NK cells (p). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments (a, c, d, k, o) or are the mean ± s.d. of three (e–h, l, m, p) or five (b, j, n) independent experiments. The p values (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01) were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test (b, e, g, h, j, l–n) or one-way ANOVA (p)