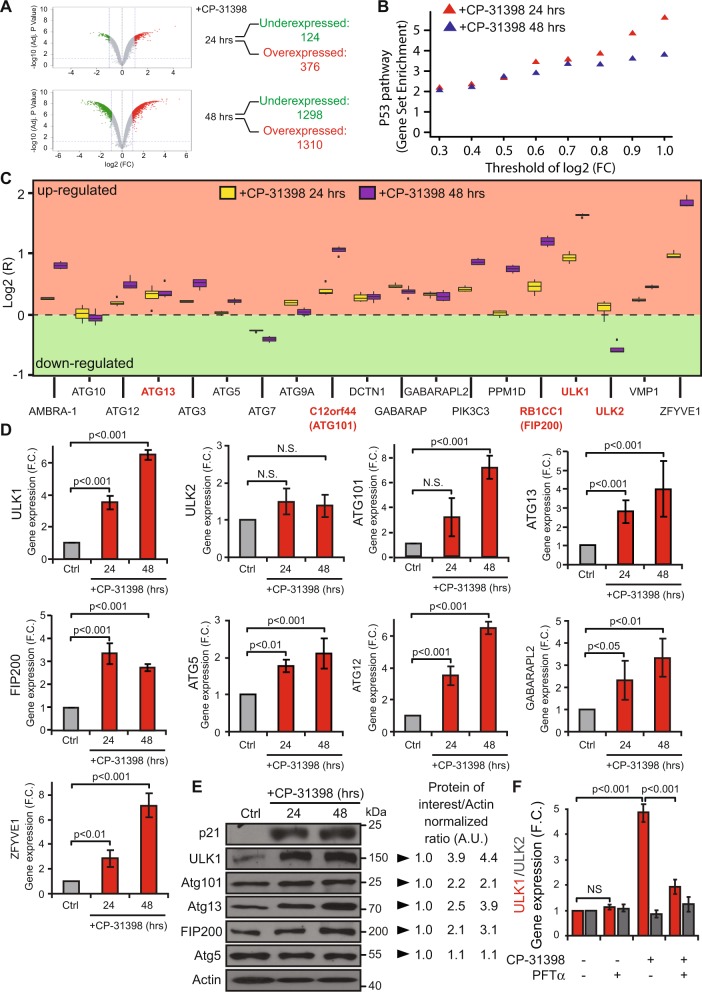
Fig. 2. The reactivation of p53 transcriptional activity by CP-31398 leads to the overexpression of genes belonging to the ULK complex and involved in autophagy initiation.
a Volcano-plot obtained from microarray analysis of MDA-MB231 cells treated with CP-31398. The number of overexpressed and downregulated genes (F.C. > 2; p < 0.05) is indicated. b Genes belonging to the p53 pathway/network (hallmark_P53_pathway; GSEA) are enriched in overexpressed genes following CP-31398 treatment (24 and 48 h). c Targeted analysis of microarray results using a pre-established list of genes involved in autophagosomes formation. Most of these genes are upregulated following 24–48 h CP-31398 treatment. Genes indicated in red encode proteins belonging to the ULK complex. d RT-qPCR validation of ULK1, ULK2, ATG101, ATG13, FIP200, ATG5, ATG12, GABARAPL2, and ZFYVE1 expression following CP-31398 treatment (24 and 48 h) compared to untreated cells (F.C. fold-change). e CP-31398 treatment (24–48 h) increases the expression of several proteins belonging to the ULK complex (ULK1, ATG101, ATG13, FIP200). ATG5 was used as a control. The normalized ratio protein of interest/Actin was calculated by densitometry analysis and display. Data are representative of three independent experiments. f PFT-α (an inhibitor of p53 transcriptional activity) inhibits CP-31398-dependent induction of ULK1 expression, while ULK2 expression is not affected. Data (d, f) are the mean ± s.d. of five independent RT-qPCR experiments performed in duplicate. The p values (d, f) were determined by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test. (NS non-significant)