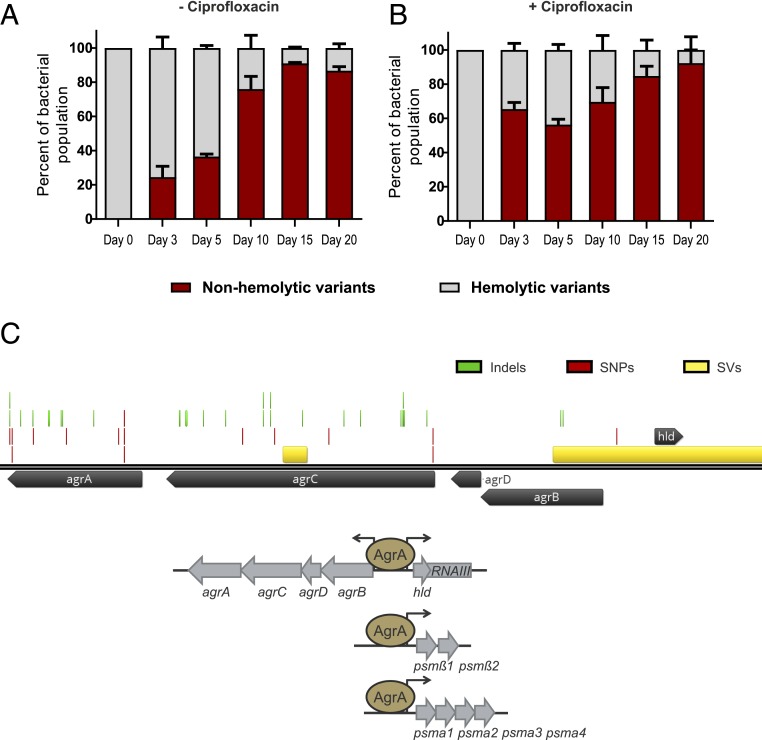
Fig. 1.
Evolution of agr mutants in vitro. Long-term evolution of HG001 (A) without and (B) with sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ciprofloxacin (0.125 µg/mL). Percentage of nonhemolytic and hemolytic subpopulations was determined based on colony phenotype on blood agar. (C) Representation of the mutations occurring within the agr locus after evolution in an aerobic environment. Mutations comprise single residue insertions or deletions (indels), single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), or larger deletions, i.e., structural variants (SVs). The agr locus comprises the agrBDCA operon and the divergently transcribed RNAIII molecule which also encodes δ-hemolysin (Hld). The autoinducing peptide (AIP) is encoded by agrD. Accumulation of extracellular AIP results in autophosphorylation of the histidine kinase AgrC and phosphotransfer to the response regulator AgrA. Phosphorylated AgrA triggers transcription of its own operon (agrBDCA) as well as RNAIII. AgrA also binds to the promoters of the psm operons, psmα and psmβ coding for the PSMs; PSMα1–4 and PSMβ1–2, respectively.