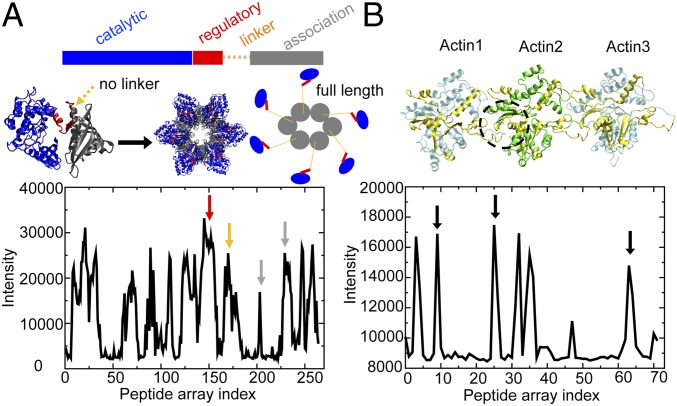
Fig. 1.
Structure and experimental peptide array data for CaMKIIβ and actin. (A) The crystal structure of a CaMKII construct without linker (PDB ID code 3SOA). (Left) CaMKII monomer; (Middle) CaMKII dodecamer; (Right) in comparison, a full-length CaMKII construct with linker displays an extended structure. The intensity profile of CaMKIIβ peptides binding to actin in the peptide arrays is shown below. Multiple CaMKII domains show binding with actin (red arrow, regulatory domain; orange arrow, linker; gray arrow, association domain). (B) The structure of 3 consecutive actins (Actin1 to Actin3) in a near-atomic model for an actin filament (PDB ID code 3J8I). The intensity profile of actin peptides binding to CaMKIIβ in the peptide arrays is shown below. Actin regions showing a high degree of binding with CaMKIIβ are colored in yellow on the ribbon diagram. The dashed black circle represents the hydrophobic cleft of F-actin, a conserved binding pocket for many actin-binding proteins (shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S1). Corresponding peptide signals are identified by black arrows.