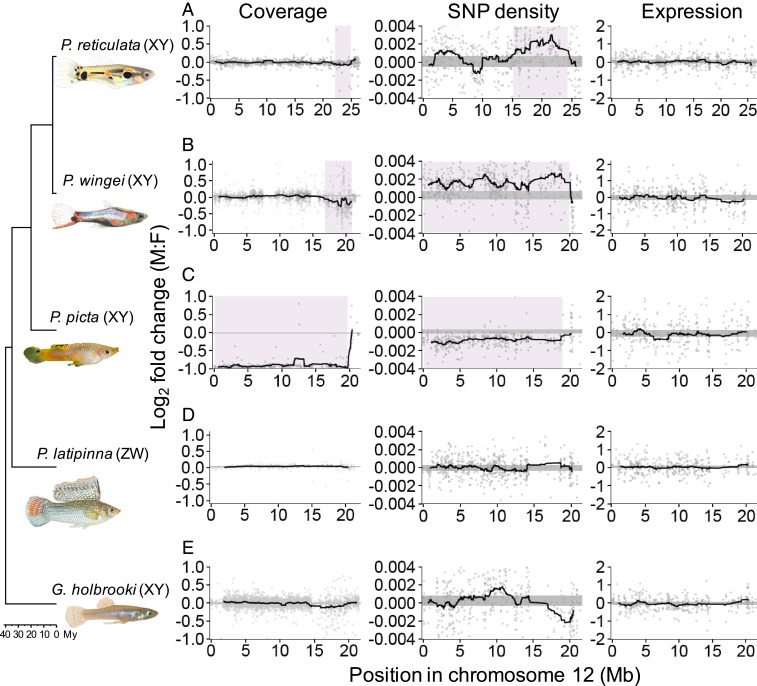
Fig. 1.
Differences between the sexes in coverage, SNP density, and expression across the guppy sex chromosome (P. reticulata chromosome 12) and syntenic regions in each of the target species. X. hellerii chromosome 8 is syntenic, and inverted, to the guppy sex chromosome. We used X. hellerii as the reference genome for our target chromosomal reconstructions. For consistency and direct comparison to P. reticulata, we used the P. reticulata numbering and chromosome orientation. Moving average plots show male-to-female differences in sliding windows across the chromosome in P. reticulata (A), P. wingei (B), P. picta (C), P. latipinna (D), and G. holbrooki (E). The 95% confidence intervals based on bootsrapping autosomal estimates are shown by the horizontal gray-shaded areas. Highlighted in purple are the nonrecombining regions of the P. reticulata, P. wingei, and P. picta sex chromosomes, identified through a significant deviation from the 95% confidence intervals.