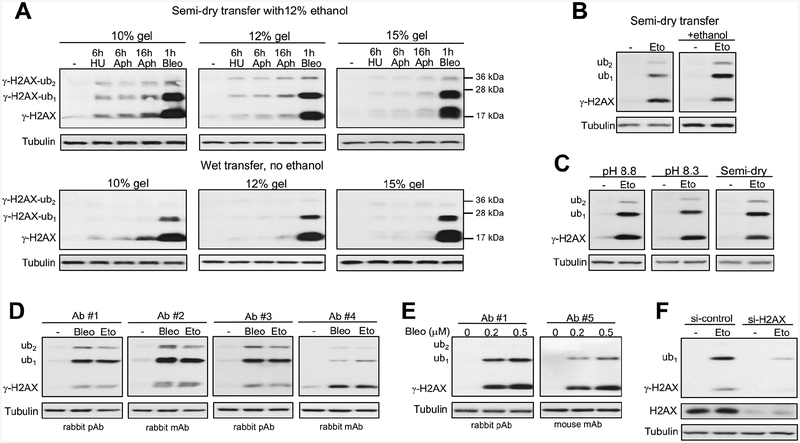
Figure 1. Technical factors affecting detection of ubiquitinated forms of Ser139-phosphorylated histone H2AX (γ-H2AX) by western blotting.
Panels A-C used antibodies #1. (A) Impact of gel polyacrylamide percentage and transfer conditions to PVDF membranes. Treatments of H460 cells: 6 h with 3 mM hydroxyurea (HU), 6 or 16 h with 5 μM aphidicolin (Aphi) or 1 h with 5 μM bleomycin (Bleo). All γ-H2AX images had 5 s film exposures. (B) Ethanol effect in semi-dry transfer. IMR90 cells were treated with 40 μM etoposide (Eto) for 1 h. (C) Comparison of wet (pH 8.2 and pH 8.8) and semi-dry transfers using 12% ethanol-containing buffers (10 s film exposures for all γ-H2AX images). IMR90 cells were treated with 40 μM etoposide for 1 h. (D) Effectiveness of different antibodies using semi-dry transfer with 12% ethanol. Normal human keratinocytes were treated for 1 h with 30 μM etoposide or 0.5 μM bleomycin. Antibodies #1–3: 1:1000 dilutions and 5 s exposures, antibody #4: 1:1000 dilution and 60 s exposure. (E) Comparison of antibodies #1 and #5 (both at 1:1000 dilutions) in H460 cells treated with bleomycin for 1 h. (F) γ-H2AX blot (Ab#1) in control and H2AX-depleted IMR90 cells treated with 100 μM etoposide for 1h.