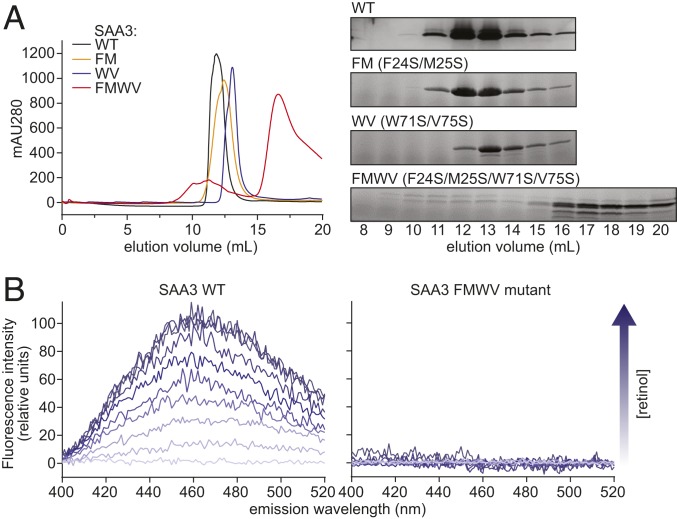
Fig. 5.
Mutations in helices α1, α2, and α3 disrupt SAA3 packing and retinol binding. (A) Wild-type or mutant SAA3 proteins were expressed, purified, and analyzed by size-exclusion chromatography. (Left) Size-exclusion chromatography profiles of wild-type and mutated SAA3. FM, WV, and FMWV denote the F24S/M25S, W71S/V75S, and F24S/M25S/W71S/V75S SAA3 mutants, respectively. (Right) Samples of peak fractions shown at the left were visualized by Coomassie blue staining after SDS/PAGE. (B) Retinol-binding assay of wild-type SAA3 (Left) or FMWV mutant (Right). 0.5 μM SAA3 protein (wild-type or FMWV mutant) was incubated with different retinol concentrations, and the fluorescence intensity was monitored following excitation at 348 nm. The arrow indicates increasing retinol concentrations (0 to 5 μM).