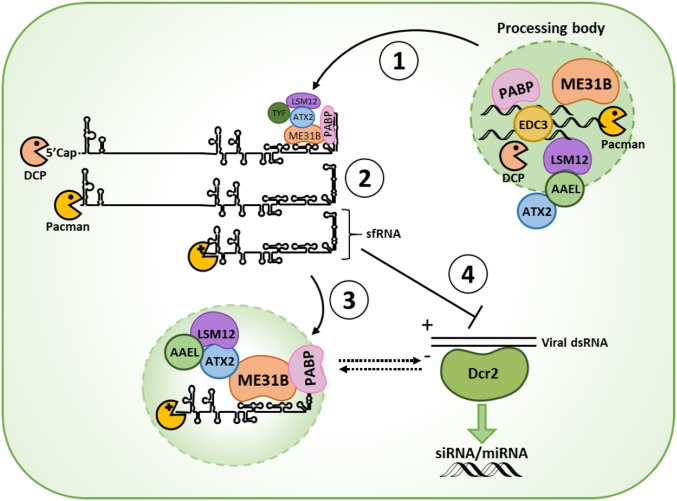
Fig. 6.
Mechanistic model of sfRNA during flavivirus infection of mosquitoes. (Step 1) In the early stage of replication, (+) strand vgRNA molecules bind ME31B (ortholog of human DDX6) via the 3′ untranslated region (UTR) to recruit processing-body (PB) components to viral replication complexes. (Step 2) Recruitment of PB components involved in decapping and mRNA degradation, including decapping enzymes (DCPs) and the exoribonuclease Pacman (ortholog of human XRN1), induces decapping of free (+) viral genomic RNA followed by degradation by Pacman. Pacman stalls on resistant stem-loop RNA structures in the 3′ untranslated region (UTR), leading to the formation of sfRNA. (Step 3) SfRNA competes with the 3′ UTR for binding of PB-associated proteins and sequesters these proteins into cytoplasmic foci. (Step 4) SfRNA suppresses the RNAi response either directly by acting as a decoy substrate for Dcr2, or indirectly by remodeling PBs and associated RNA silencing complexes. PBs, processing bodies; Dcr2, Dicer2; PABP, poly-(A) binding protein; DCP, decapping enzyme; SL, stem-loop; DB, dumbbell; AAEL, AAEL018126.