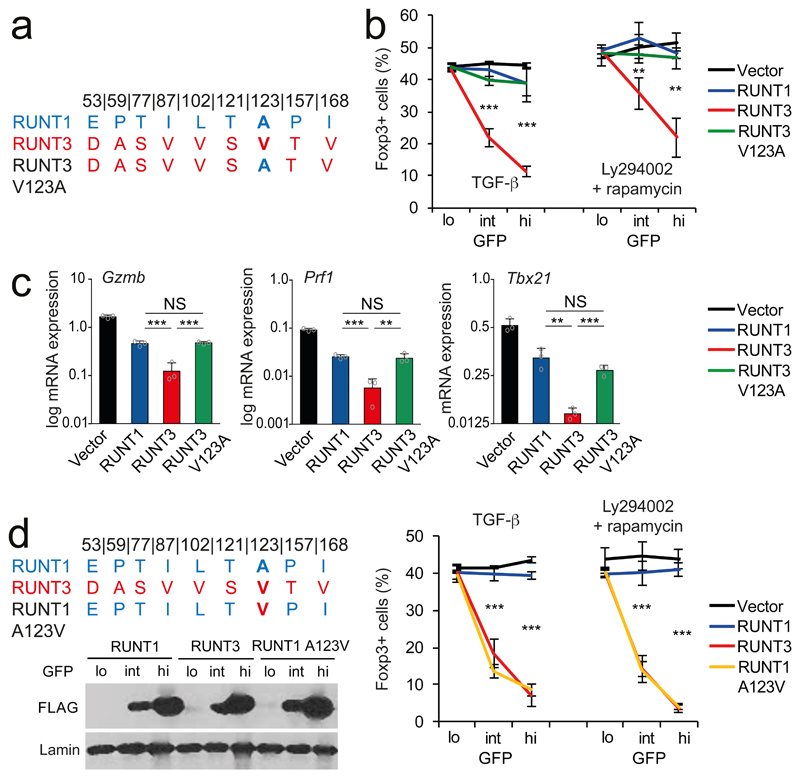
Fig. 6. Identification of residues that functionally distinguish paralogous RUNT domains.
a) RUNT1 and -3-specific amino acids, numbers refer to position in mouse RUNX1. With the exception of I168, none of these contact DNA.
b) Replacement of RUNT3 V123 by the RUNT1 A123 (V123A) weakens the dominant negative activity of RUNT3. Mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 by two-tailed T test between RUNT3 and RUNT3 V123A.
c) V123 affects the regulation of the RUNX target genes Gzmb, Prf1, and Tbx21. Mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. Results for all RUNT domain constructs were significantly different from control vector (P<0.001 by two-tailed Student's T test). ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001 by two-tailed T test. NS = not significant.
d) RUNT1 A123V is a more potent antagonist of Foxp3 induction in CD4 T cells than RUNT1 at matched levels of expression (as judged by FLAG-RUNT immunoblotting of GFP-lo/int/hi). Mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments. *** P<0.001 by two-tailed T test between RUNT1 and RUNT1 A123V.