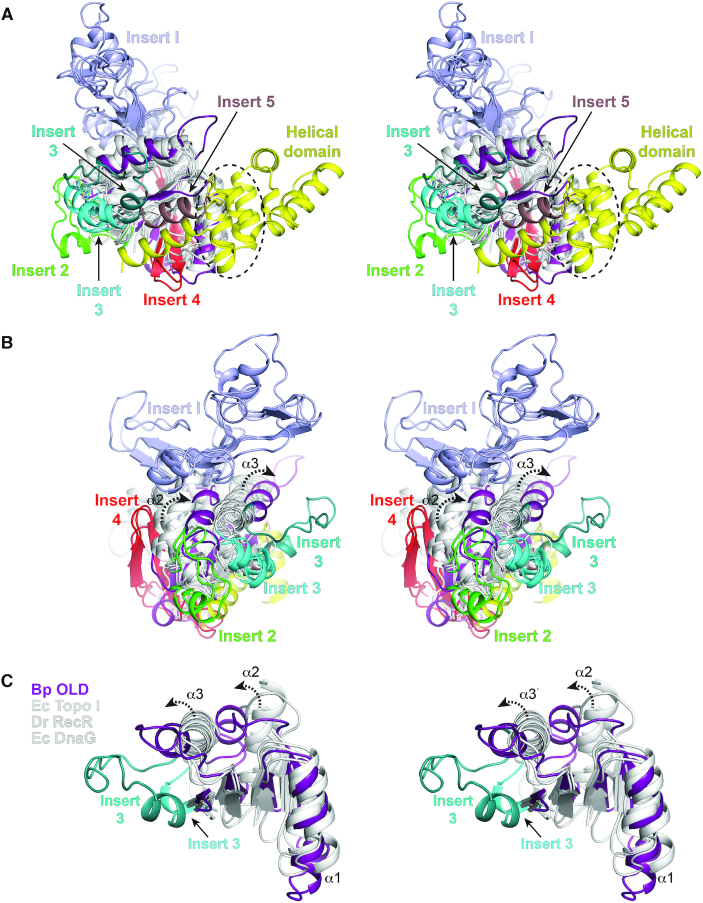
Figure 3.
Topological differences in present in Class 2 OLD Toprim domains. (A, B) Structural superposition of Toprim domains. Side (A) and end (B, rotated 90°) views are shown in stereo. Structural alignment includes the following: Geobacillus kaustophilus conserved hypothetical protein (PDB: 2FCJ), Escherichia coli DnaG primase (PDB: 3B39), Aquifex aeolicus putative ribonuclease M5 (PDB: 1T6T), Deinococcus radiodurans RecR (PDB: 1VVD), Thermotoga maritima Topoisomerase I (PDB: 2GAJ), Escherichia coli Topoisomerase I (PDB: 1MW9), Homo sapiens Topoisomerase IIB (PDB: 3QX3), Streptococcus pneumoniae IV topoisomerase (PDB: 4I3H), Escherichia coli Topoisomerase III (PDB: 2054), Archaeoglobus fulgidus reverse gyrase (PDB: 1GKU), and Thermotoga maritima reverse gyrase (PDB: 4DDU). Toprim cores are colored white with Inserts 1–5 individually labeled (see Supplementary Figures S8 and S9). Bp Toprim and helical domains are colored purple and yellow respectively. Dashed circle in (A) denotes the position of the glutamate helix. (C) Stereo view of α2 and α3 helical shifts (dashed arrows) in Bp OLD Toprim core relative to the Toprim central β-sheet. Central segments of Escherichia coli (Ec) Topoisomerase I, Deinococcus radiodurans (Dr) RecR and Escherichia coli DnaG are shown for comparison. Alternative position of Insert 2 in Bp OLD is also shown.